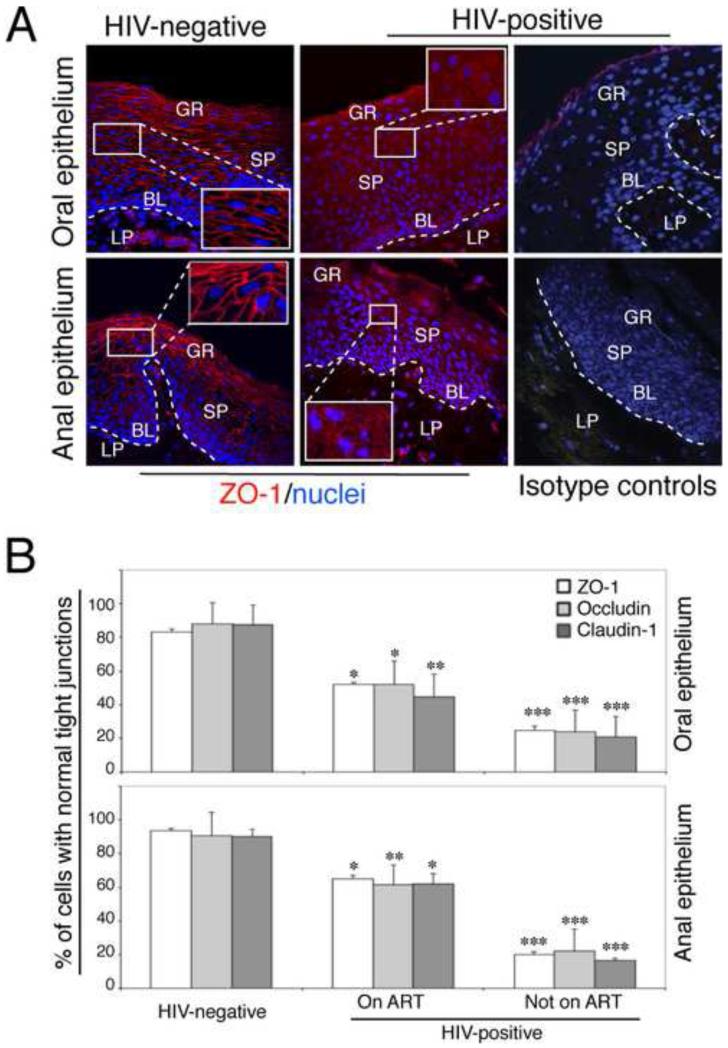
Fig. 1.
Disruption of TJs of HIV-infected oral and anal mucosal epithelia. (A) Oral and anal biopsies from HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected individuals were immunostained for ZO-1 (red). As a negative control, sections were stained with rabbit IgG. GR, granulosum; SP, spinosum; BL, basal; LP, lamina propria. Nuclei are stained in blue. Original magnification was ×400. Representative immunofluorescence images are shown. (B) For quantitative evaluation of TJ protein expression in oral and anal tissues of HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected individuals, epithelial cells expressing ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-1 in ring-shaped patterns were counted from 10 randomly-selected regions of mucosal epithelia. Cells were counted in 10 fields of each tissue section. Results were obtained from oral biopsies (4 HIV-uninfected, 6 HIV-infected on ART and 6 HIV-infected not on ART) and anal biopsies (5 HIV –negative, 6 HIV-infected on ART and 3 HIV-infected not on ART). Results are represented as a percentage of epithelial cells with a normal pattern (ring shape) of ZO-1, occludin and claudin-1 expression. Error bars represent standard errors of the means. * P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, all compared with the HIV-uninfected control group.