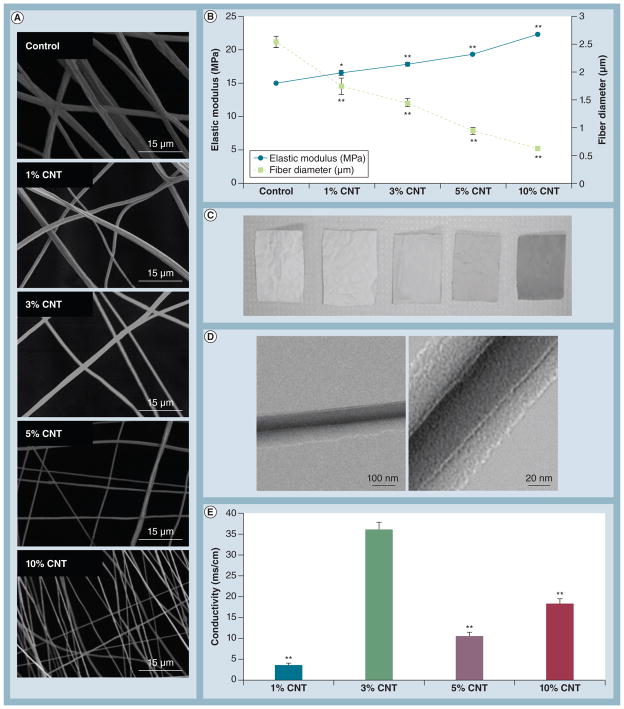
Figure 2. Optimization of carbon nanotube loading concentration.
(A) Representative scanning electron microscopy images of mats spun for 20 min demonstrated a decrease in fiber diameter with increasing CNT loading concentration. (B) An inverse correlation between elastic modulus and fiber diameter was observed with increasing CNT concentration (n = 9 samples/group for elastic modulus). *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.001 versus control. (C) Fiber mats containing higher CNT concentrations were markedly darker, indicating successful incorporation of CNTs. (D) Representative images of CNTs embedded within polymer fibers by transmission electron microscopy for the 5%CNT group. (E) Overall, electrical conductivity correlated with CNT concentration except for mats containing 3% CNTs, which exhibited excellent conductivity (n = 3 samples/group). **p < 0.01 versus 3%CNT.
CNT: Carbon nanotube.