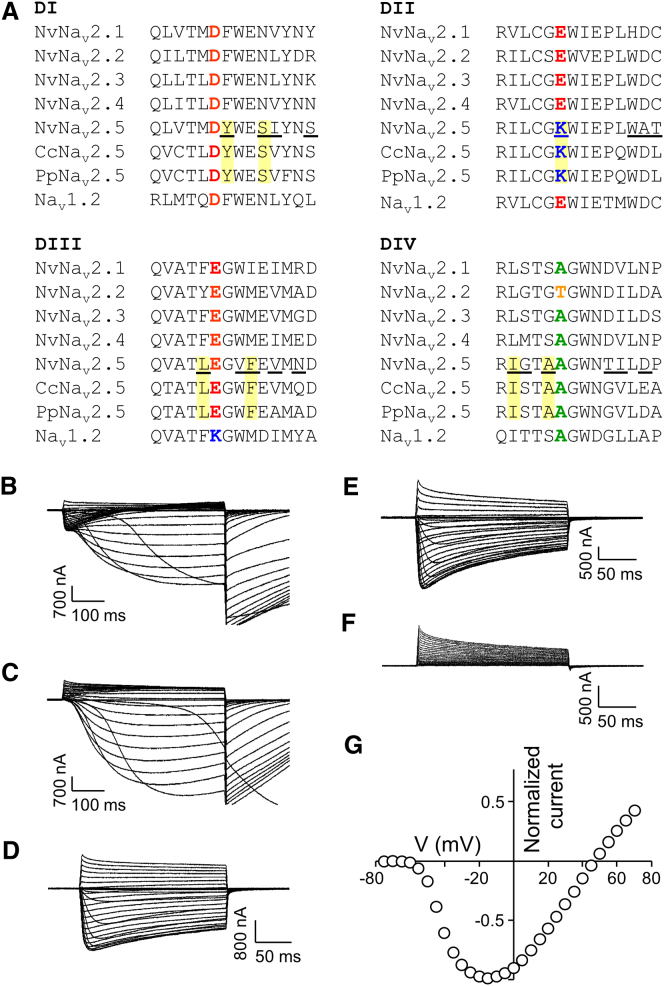
Figure 3.
Sequence Alignment of NvNav2 Channels and Current Recordings from NvNav2.1DKEA and NvNav2.1NvNav2.5(p−loops) Channels Expressed in Xenopus Oocytes
(A) Alignment of the pore-loop regions of the five N. vectensis (Nv) channels (see also Figure S3 for spatiotemporal expression of Nav2 cnidarian channels), as well as a channel from the medusae P. penicillatus (Pp) and C. capillata (Cc) and the mammalian brain channel Nav1.2. Substitutions of NvNav2.1NvNav2.5(p−loops) are underlined and substitutions unique to the Nav2.5 channel subfamily are in yellow boxes. For current recordings the oocytes were clamped at −80 mV holding potential and currents were elicited by 200 or 500 ms depolarizing voltage pulses from −75 mV to either 50 or 70 mV.
(B) NvNav2.1DKEA in ND96 bath solution.
(C) NvNav2.1DKEA with choline substituting for Na+ in the bath solution.
(D) NvNav2.1DKEA with Ca2+ in the bath solution chelated by EGTA.
(E and F) NvNav2.1NvNav2.5(p−loops) in ND96 bath solution (E) and with choline substituting for Na+ (F).
(G) Current-voltage relations of NvNav2.1NvNav2.5(p−loops) (Erev = 46.5 ± 1.2 mV; n = 19). Each point represents mean ± SEM of n cells (see Figure S2 for analysis of the SF in NvNav2.1NvNav2.5(p−loops)).