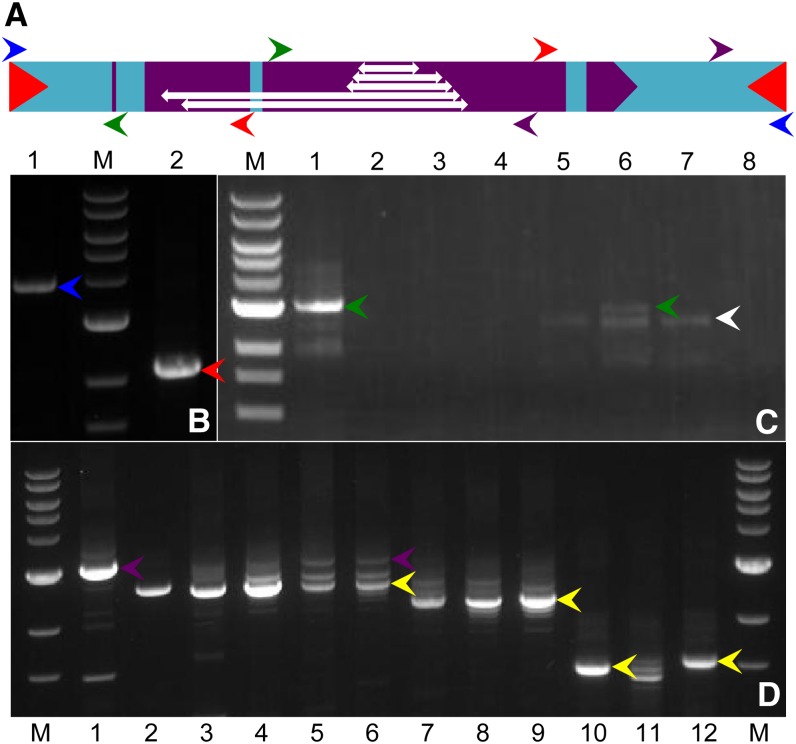
Figure 7.
PCR Amplification of cTED and dTED from bz-m175.
(A) Color-coded PCR primers in the parental TED sequence. dTED deletions are shown as double-headed arrows (from top to bottom, dTED20, dTED18, dTED13, dTED2, and dTED4).
(B) Amplification of bz-m175 DNA. Lane 1, a TIR single primer (blue arrows in [A]) amplifies the full-length element (blue arrowhead); lane 2, divergent internal primers (red arrows in [A]) produce a band of the expected size for a circular element (red arrowhead).
(C) Amplification with TED divergent primers (green arrows in [A]) of cTED and dTED elements (green and white arrowheads, respectively) in the trTED line GT30 (lane1) and in the bz-m progeny from a GT30 × dTED20 cross (lanes 5 to 7). No products are amplified in the TED-minus bz progeny from the same cross (lanes 2 to 4) or in the dTED20 line (lane 8).
(D) Amplifications with TED primers (purple arrows in [A]) of cTED (purple arrowheads) and corresponding dTED products (yellow arrowheads) from bz-m175/bz-R (lane 1) and four different trTED/dTED segregating lines. Lanes 2 to 6, dTED18; lanes 7 to 9, dTED13; lane 10, dTED2; lanes 11 and 12, dTED4; M, 1-kb DNA ladder.