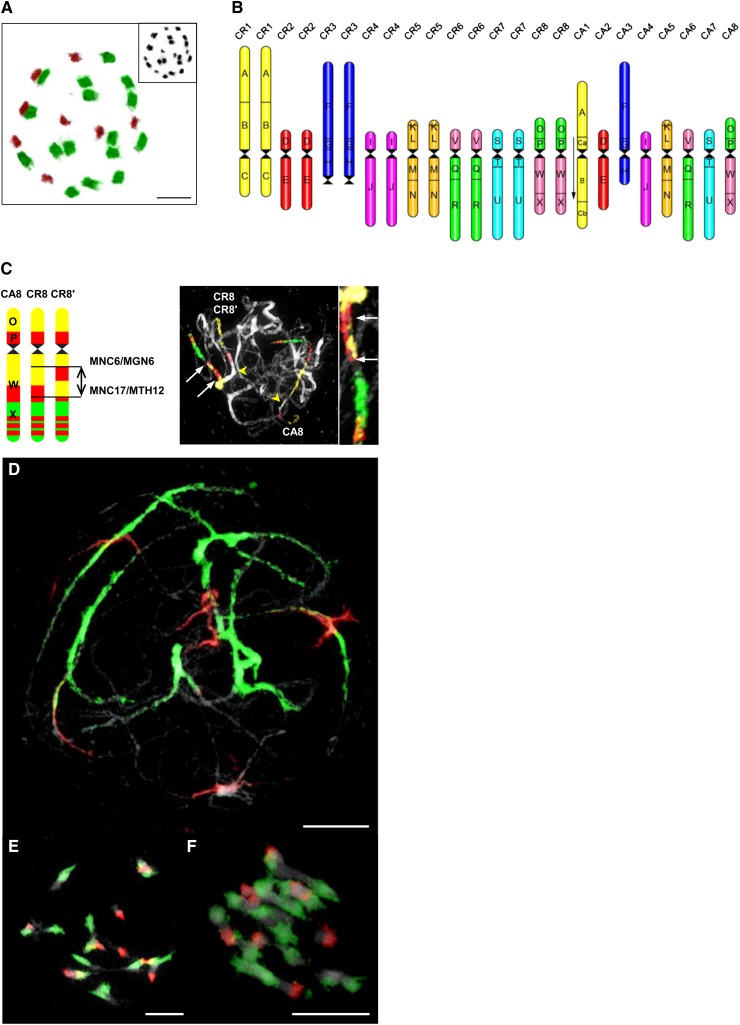
Figure 2.
Genome Structure of the Triploid Hybrid C. × insueta (2n = 3x = 24).
(A) GISH revealing eight chromosomes of C. amara (red fluorescence) and 16 chromosomes of C. rivularis (green fluorescence). DAPI-stained chromosome spread shown in the inset.
(B) Comparative ideogram of C. × insueta based on comparison with the eight ancestral chromosomes and 24 genomic blocks (A to X) of the ACK (Schranz et al. 2006) and the reconstructed karyotypes of C. amara (chromosomes CA1 to CA8) and C. rivularis (CR1 to CR8).
(C) The 2.4-Mb paracentric inversion on the CR8' homolog (blocks O, P, W, and X) in plants from subpopulation #4. Arrows point to the inverted region, and arrowheads indicate centromeres.
(D) to (F) GISH revealing chromosomes of C. amara (red) and C. rivularis (green) at pachytene (D), diakinesis (E), and metaphase I (F). Bars = 5 µm