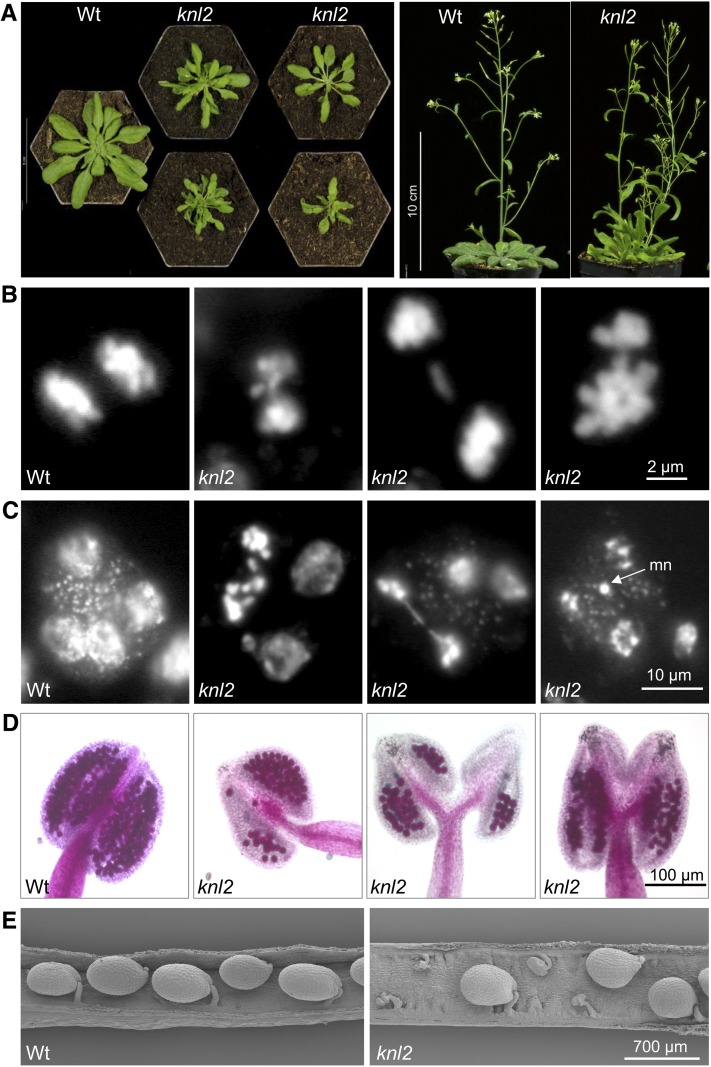
Figure 4.
Phenotype of the knl2 Mutant.
(A) Comparison of the phenotype of knl2 mutant with that of the wild-type (Wt). Plants were grown for 4 weeks (left panel) or 6 weeks (right panel) on soil.
(B) Mitotic anaphases of the wild type and of a knl2 mutant plant with bridges and lagging chromosomes. Among 400 anaphases of the wild type and 1500 anaphases of the knl2 mutant, 0.5 and 10% showed bridges, respectively.
(C) Pollen tetrads of the wild type and of a knl2 mutant with bridges and micronuclei (mn), respectively.
(D) Anthers of the wild type and of a knl2 mutant after Alexander staining to indicate viable pollen.
(E) Scanning electron microscopy images of siliques of the wild type and a knl2 mutant.