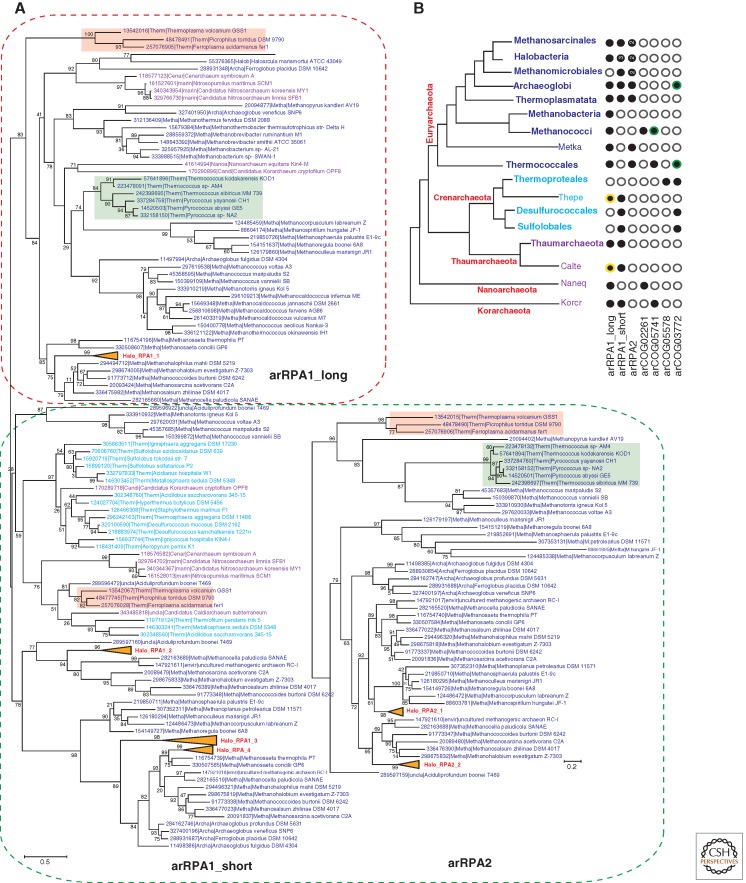
Figure 6.
Phylogenetic analysis of the RPA family in archaea and eukarya. The designations and the method of tree reconstruction are as in Figure 2. (Green) The Thermococcales branches; (pink) the Thermoplasmata branches. Halobacterial branches are collapsed and numbered as follows: for arRPA1 from Halo_RPA1_1 to Halo_RPA1_4 and for arRPA2 from Halo_RPA2_1 to Halo_RPA2_2. “Long” RPAs are outlined by the red dotted line and “short” RPAs by the green dotted line. (A) Phylogenetic trees of the RPA1 and RPA2 families. RPA1 corresponds to COG1599 (167 sequences in total, 89 aligned positions), and RPA2 corresponds to COG03390 (76 sequences in total, 149 aligned positions). (B) The phyletic patterns of SSB/RPA proteins and their homologs in archaea. The designations are as in Figure 4C. (In panel B, circles with a yellow outline denote) RPA proteins from several organisms that could not be confidently aligned and thus are not present in the corresponding tree but included into the phyletic pattern. (Green outline) Those that do not include all representatives in the corresponding lineage.