Figure 7.
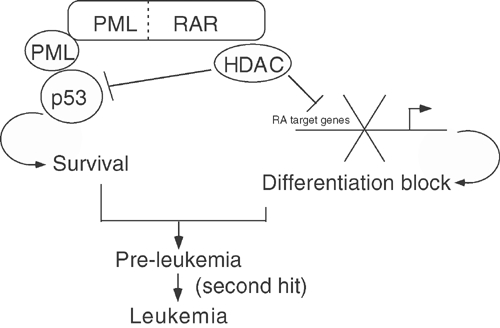
PML–RAR acts as an HDAC-dependent inhibitor of pathways regulated by wild-type PML and RAR. PML–RAR acts as a bifunctional protein: (i) it inhibits the transcription of RA target genes in the presence of physiological concentrations of ligand, thus blocking myeloid differentiation; and (ii) it inhibits p53 function (in a manner requiring wild-type PML), allowing enhanced survival of APL blasts. Both differentiation block and enhanced survival are mediated by recruitment of HDAC by the fusion protein.
