Figure 4.
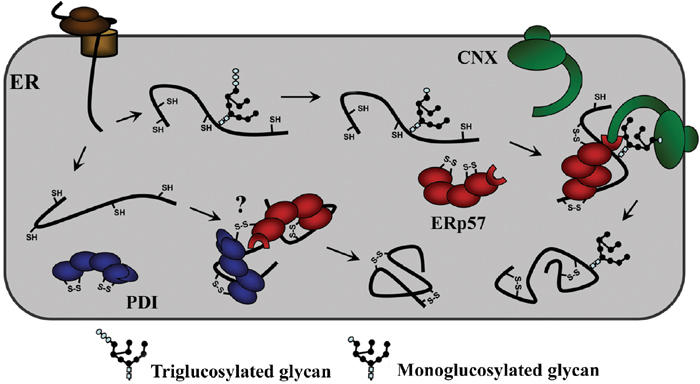
Model of the interaction of monoglucosylated folding intermediates with calnexin and ERp57. The monoglucosylated substrate binds to the chaperone through both lectin–oligosaccharide interactions as well as polypeptide-based associations. The terminal glucose residue of the substrate binds to the lectin site of calnexin within its globular domain, while the arm-like P-domain recruits ERp57, by binding to its C-terminal domain, and brings it into proximity with the polypeptide where it will catalyze disulfide bond formation and isomerization. The model also raises the possibility of ERp57 interacting with PDI through the formation of intermolecular disulfide linkages.
