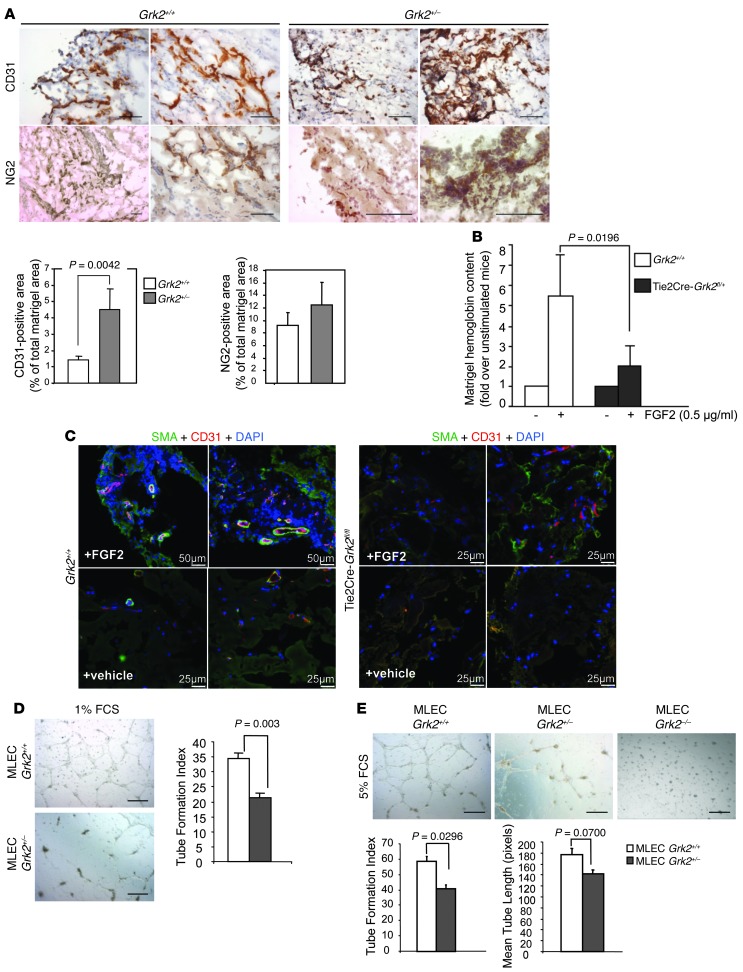
Figure 2. Endothelial GRK2 protein levels regulate vascular morphogenesis.
(A–C) Angiogenesis in mice with global or endothelial-specific reduction of GRK2 expression is characterized by a lack of functional vessels, concomitant with the occurrence of aberrant vessel-like structures with a poor mural coverage. Sections of FGF2-embeded Matrigel plugs excised (A) from WT Grk2+/+ and global Grk2+/– or (C) from Tie2Cre-Grk2fl/fl mice were analyzed by immunohistochemistry, and the density of invasion by either endothelial or mural cells was determined with (A) anti-CD31 or anti-NG2 or (C) SMA antibodies, respectively, as detailed in Methods. Ratios of CD31-positive cells to total DAPI-stained cells in FGF2-stimulated WT Grk2+/+ and Tie2Cre-Grk2fl/fl mice were 0.22 ± 0.06 and 0.58 ± 0.28, respectively. (B) Endothelial GRK2 downmodulation is sufficient to impair the functionality of angiogenic vessels. The angiogenic response in WT or Tie2Cre-GRK2 f/+ mice was determined as in Figure 1A. Data from 12 animals for each condition in 4 independent experiments are shown. (D and E) ECs with deficient GRK2 expression are less competent to form capillary-like networks in vitro. MLECs from WT (Grk2+/+), global hemizygous (Grk2+/–), or endothelial-specific (Tie2Cre-Grk2fl/fl) GRK2 knockout mice were seeded on Matrigel-coated wells in the presence of (D) 1% FCS or (E) 5% FCS. Photographs were taken after 16 to 18 hours in culture (original magnification, ×5), and formation of tubular networks was quantified as described in Methods. Data were obtained from 2 to 3 independent assays performed in duplicate. Scale bar: 100 μm (A); 25 μm (C, Tie2Cre-Grk2fl/fl and vehicle-treated Grk2+/+); 50 μm (C, FGF2-treated Grk2+/+); 500 μm (D and E).