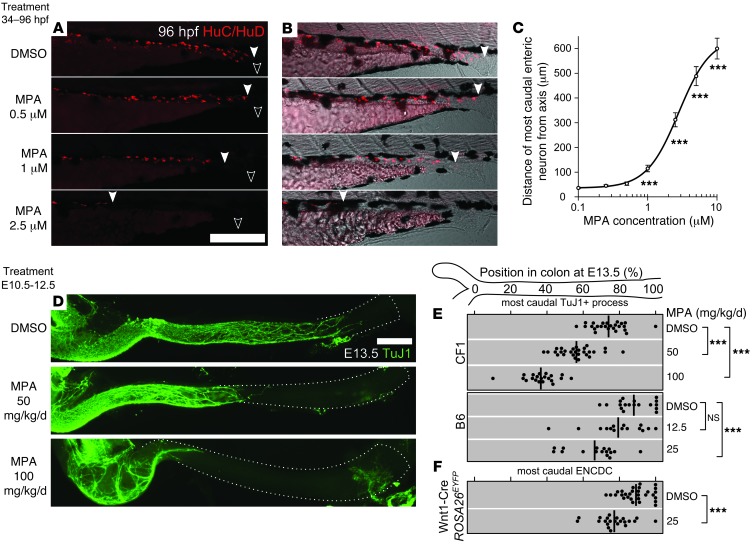
Figure 1. MPA inhibited ENS development in developing zebrafish and mouse.
(A–C) Developing WT zebrafish were exposed to DMSO or MPA from 34 to 96 hpf. (A) Larvae (N > 200) were immunostained for neuronal marker HuC/HuD. (B) Images in A merged with transmitted light. Filled arrowheads denote most caudal enteric neuron; open arrowheads denote vents. (C) Average uncolonized distal intestine, plotted vs. MPA dose and compared with control. (D–F) MPA exposure by maternal intraperitoneal injection from E10.5 to E12.5 impaired enteric neuron colonization of the mouse hindgut at E13.5 (D), as visualized by the neuronal marker TuJ1 (left side, ileocecal junction; dotted line, colon outline). The position within each E13.5 colon of the most caudal (E) neuronal process (marked by TuJ1) or (F) ENCDC cell body (ascertained by the lineage marker EYFP or by SOX10 staining in EYFP– littermates) in each E13.5 fetus is plotted for each MPA dose and mouse strain (thick lines denote mean). Scale bars: 250 μm (A and B); 1 mm (D). ***P < 0.001, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test (C); ANOVA and t test (E and F).