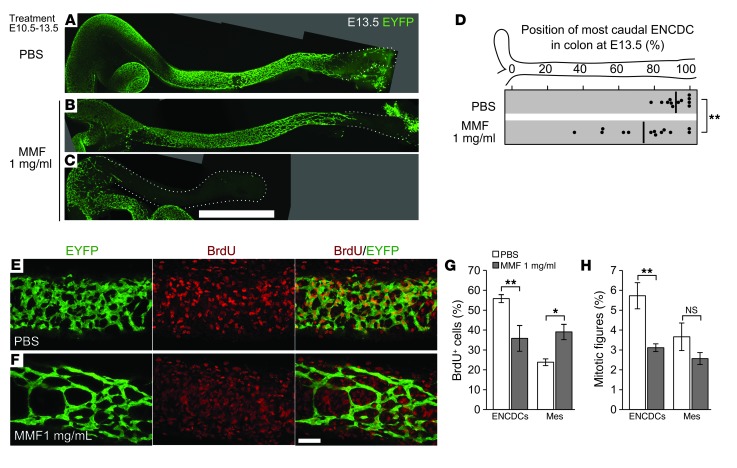
Figure 3. MMF treatment reduces ENCDC migration and DNA synthesis in vivo.
(A–D) Oral treatment of pregnant B6 dams with MMF from E10.5 to E13.5 reduced the colonization of the hindgut at E13.5. Shown are stitched maximum-intensity projections of untreated (A), mildly affected (B), and severely affected (C) fetal colons with EYFP-marked ENCDCs, demonstrating MMF’s inhibitory effect on ENCDC wavefront migration in vivo. Dotted lines denote outline of bowel. (D) The position within each E13.5 colon of the most caudal ENCDC cell body (ascertained by EYFP or by SOX10 staining in EYFP– littermates) is plotted for each treatment (thick lines denote mean). (E and F) 8-μm-thick maximum-intensity projections of EYFP- and BrdU-labeled E13.5 colons. (G) Counting of BrdU+ cells within the volumes in F demonstrated a reduced proportion of BrdU+ ENCDCs and an increased proportion of BrdU+ mesenchymal cells after MMF treatment. mes, non-ENCDC mesenchyme. (H) Counting of mitotic figures showed that the proportion of ENCDCs undergoing mitosis was reduced, while the mitotic index of the mesenchyme was not significantly changed. Scale bars: 1 mm (A–C); 50 μm (E and F). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, Student’s t test (D); ANOVA (G); ANOVA on log-transformed values (H).