Figure 3.
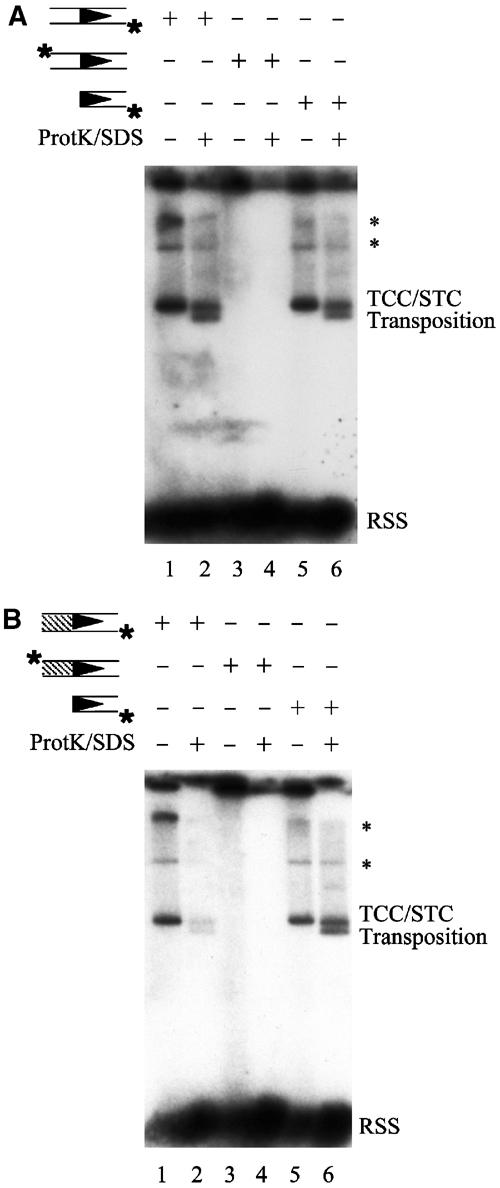
Release of hairpinned coding ends is required for target capture. (A) As indicated above the gel, target capture was carried out as in Figure 2B using either intact RSS substrates (VDJ100/101, VDJ132/133) labeled on the donor strand (lanes 1 and 2), intact RSS substrates (VDJ100/101, VDJ132/133) labeled on the coding strand (lanes 3 and 4), or precleaved RSS substrates (VDJ104/106, YD24/VDJ134) labeled on the donor strand (lanes 5 and 6). With intact RSS donors labeled on the donor strand, complexes detected in this assay could, in principle, consist of uncleaved TCCs, hairpin TCCs, signal-end TCCs, or any combination of these three complexes. With intact RSS donors labeled on the coding strand, complexes detected in this assay could, in principle, consist of uncleaved TCCs, hairpin TCCs, or a mixture of these two complexes. Using precleaved RSS donors labeled on the donor strand, complexes detected in this assay could only consist of signal-end TCCs. The positions of the TCC/STC mixed band and the transposition products are shown. The symbol * marks higher molecular weight bands that represent TCCs and STCs that have used concatamerized plasmids as target DNA. (B) Target capture was carried out as in (A), using either altered coding flank substrates (VDJ100.1/101.1, VDJ132.1/133.1) labeled on the donor strand (lanes 1 and 2), altered coding flank substrates (VDJ100.1/101.1, VDJ132.1/133.1) labeled on the coding strand (lanes 3 and 4), or precleaved RSS substrates (VDJ104/106, YD24/VDJ134) labeled on the donor strand (lanes 5 and 6). The positions of the TCC/STC mixed band and the transposition products are shown. The symbol * marks higher molecular weight bands that represent TCCs and STCs that have used concatamerized plasmids as target DNA.
