Figure 3.
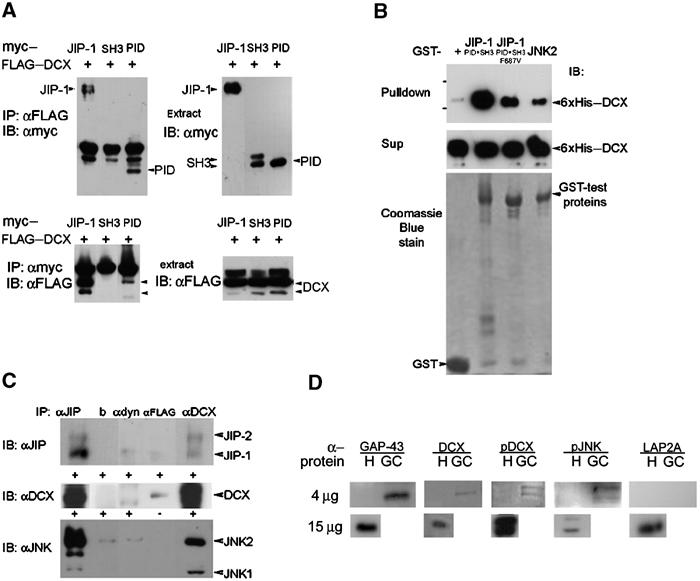
DCX interacts with JIP-1 and the interaction domain is in the DC motif and the PID domain, respectively. (A) Cells transfected with FLAG–DCX, and with myc-tagged JIP-1, the SH3 domain of JIP-1, or the PID domain of JIP-1 were subjected to immunoprecipitations using anti-FLAG antibodies (top left panel) or anti-myc antibodies (bottom left panel). The expression of each of the proteins was verified by Western blot analysis (both right panels). The interaction domain mapped within the PID domain. (B) Recombinant proteins 6xHis-tagged DCX were pulled down using the corresponding GST-tagged proteins (GST control, JIP-1 (SH3+PID domain), JIP-1 (SH3+PID domain mutated F687V), JNK2). The levels of the input proteins were similarly judged by Coomassie blue stain (lower panel) or anti-His Western blot (middle panel). (C) DCX, JIP and JNK co-immunoprecipitated from mouse brain extracts. P7 mouse brain was used for immunoprecipitations using monoclonal anti-DCX antibodies (228), anti-FLAG antibodies (Sigma), anti-dynein antibodies (Sigma), beads, or anti-JIP goat polyclonal antibodies (E19, Santa Cruz), followed by Western blot analysis using anti-JIP1 mouse monoclonal antibodies (BD Transduction Laboratories), anti-JNK2 mouse monoclonal antibodies (D-2, Santa Cruz), and anti-DCX rabbit polyclonal antibodies (Shmueli et al, 2001). The negative controls were anti-FLAG, anti-dynein, and beads only. DCX antibodies immunoprecipitated JIP-1 and JIP-2 (top panel), JIP-1 antibodies immunoprecipitated DCX (middle panel), and DCX antibodies immunoprecipitated JNK1 and JNK2 (lower panel). (D) DCX, p-DCX, and p-JNK are enriched in growth cones. Homogenates (H) (4 or 15 μg) and growth-cone preparations (GC) (4 μg) were separated on gels and Western blotted with the following antibodies: GAP-43 (positive control, enriched in growth cones), DCX, p-DCX, p-JNK (these proteins are also enriched in growth cones), and LAP2A (negative control, nuclear protein).
