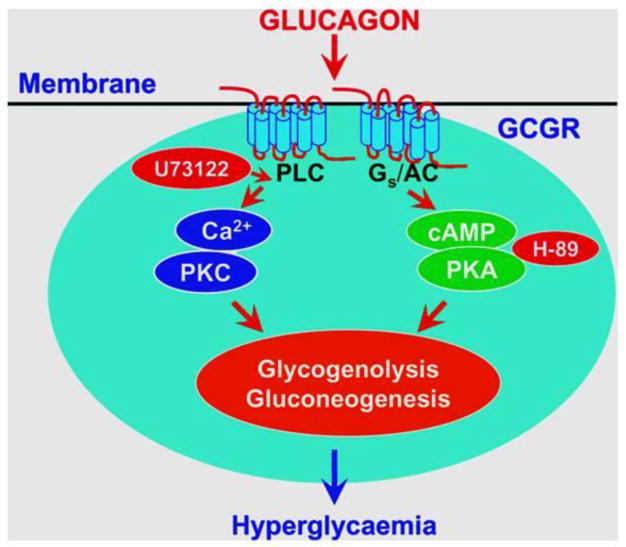
Figure 1.
Two classic G protein-coupled glucagon receptor-mediated intracellular signaling pathways in glucagon-targeted cells. To induce an effect, glucagon binds to cell surface GTP-heterotrimeric Gs protein-coupled receptors and activates phospholipase C (PLC)/IP3/Ca2+ and cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)-dependent protein kinase A (PKA) signaling. Both signaling pathways are closely involved in mediating glucagon-induced glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis, leading to hyperglycemia. Pharmacological agents known to block these two signaling pathways also inhibit glucagon-induced hyperglycemic and growth effects in target cells. Abbreviations: AC, adenylyl cyclase; GCGP, the Gs protein-coupled glucagon receptor; H-89, a selective cAMP-dependent PKA inhibitor; PKC, protein kinase C; and U73122, a selective PLC inhibitor. Reprinted with permission from Li and Zhuo [38]. Targeting glucagon receptor signaling in treating metabolic syndrome and renal injury in type 2 diabetes: theory versus promise. Clinical Science 2007; 113, 183–193.