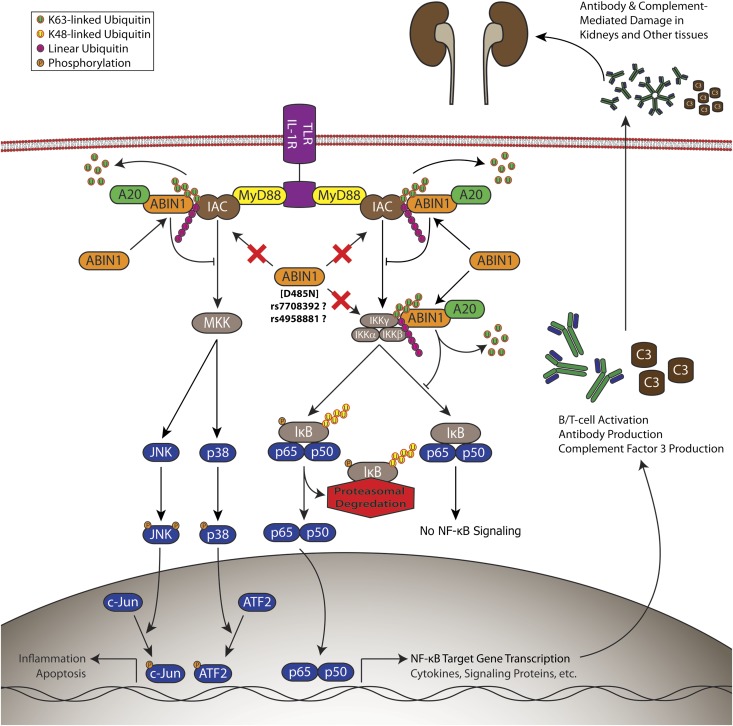
Figure 5.
Disrupted ABIN1 polyubiquitin binding contributes to the development of lupus nephritis via aberrant regulation of NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase activity. Proinflammatory gene activation is mediated by NF-κB, c-JUN, and ATF2 through TLRs and IL-1R by activation of the upstream IKK complex or MAPK kinase (MKK) activation of JNK or p38 MAPK. IKK and MKKs are activated by an inflammatory activating complex consisting of IRAKs, TRAFs, RIPs, and TAK1, among others. ABIN1 binds to K63-linked and linear polyubiquitin chains and inhibits NF-κB, c-JUN, and ATF2 by interaction with these moieties on components of the inflammatory activating complex or IKKγ. Inhibition of activators of MKKs or IKK is also facilitated by ABIN1 recruitment of the de-ubiquinating protein A20. ABIN1 mutation that disrupts these inhibitory functions contributes to LN.