Figure 2.
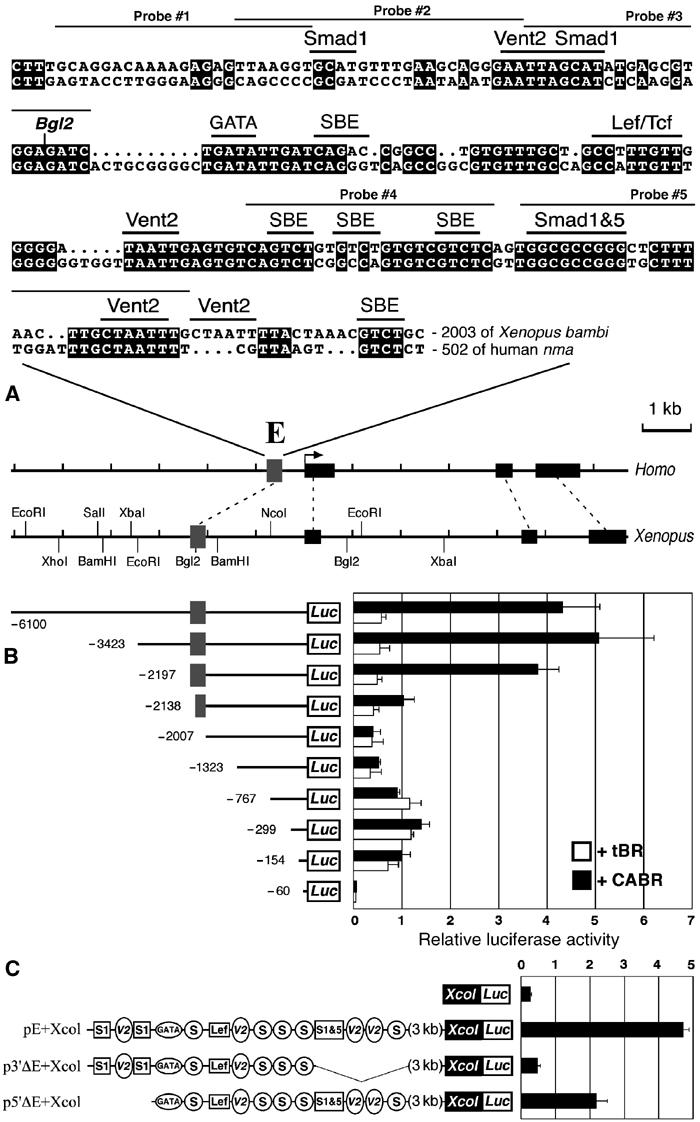
Isolation of the BRE of bambi. (A) Comparative map of Xenopus bambi and human nma genomic regions. The exons are shown as black bars, a conserved 200 bp fragment (putative enhancer) is labeled ‘E' (gray box) and its Xenopus/Homo sequence alignment is shown. The putative transcription factor binding sites are shown above the alignment. Also highlighted are sequences used to derive probes for EMSA assays. (B) Deletion analysis of the 5′ flanking region of bambi confirms that E is a BRE. Xenopus embryos were coinjected with the indicated promoter constructs and either tBR or CABR mRNA and harvested at the gastrula stage for luciferase reporter assay. (C) The bambi enhancer confers BMP inducibility to a heterologous (collagen X) minimal promoter. Xenopus embryos were coinjected with the indicated promoter constructs and CABR. Putative TF binding sites from panel A are represented schematically: S, SBE; S1, Smad1; V2, Vent2; S1&5, Smad1 and 5 motifs.
