Figure 3.
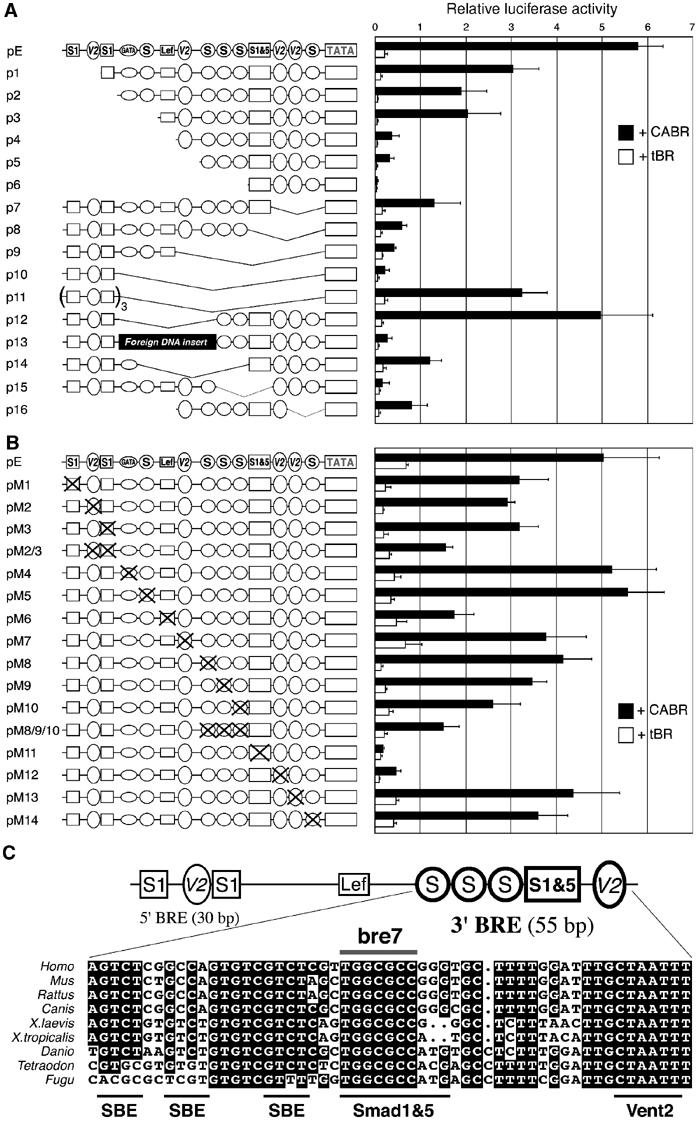
Functional dissection of the bambi enhancer. (A) Deletion and (B) point-mutation analyses of the 200 bp enhancer. Frog embryos were injected with the indicated constructs together with tBR or CABR mRNA and collected at gastrula stage for luciferase reporter assays. Putative TF binding sites are represented schematically: S, SBE; S1, Smad1; V2, Vent2; S1&5, Smad1 and 5 motifs. ‘TATA' represents the heterologous 13 bp core adenovirus E1b promoter. (C) Structure of the bambi enhancer with functionally relevant TF binding sites. The major 3′ BMP-responsive element (3′ BRE) is highlighted and its phylogenetic conservation in nine vertebrate species is shown. Putative TF binding sites are underlined. Sequences were extracted from the assembled genomic data for Homo (human), Mus (mouse), Rattus (rat), Danio (zebrafish) and Fugu (pufferfish), or from the whole-genome shotgun trace archives for Canis (dog), X. tropicalis (frog) and Tetraodon (pufferfish).
