Figure 6.
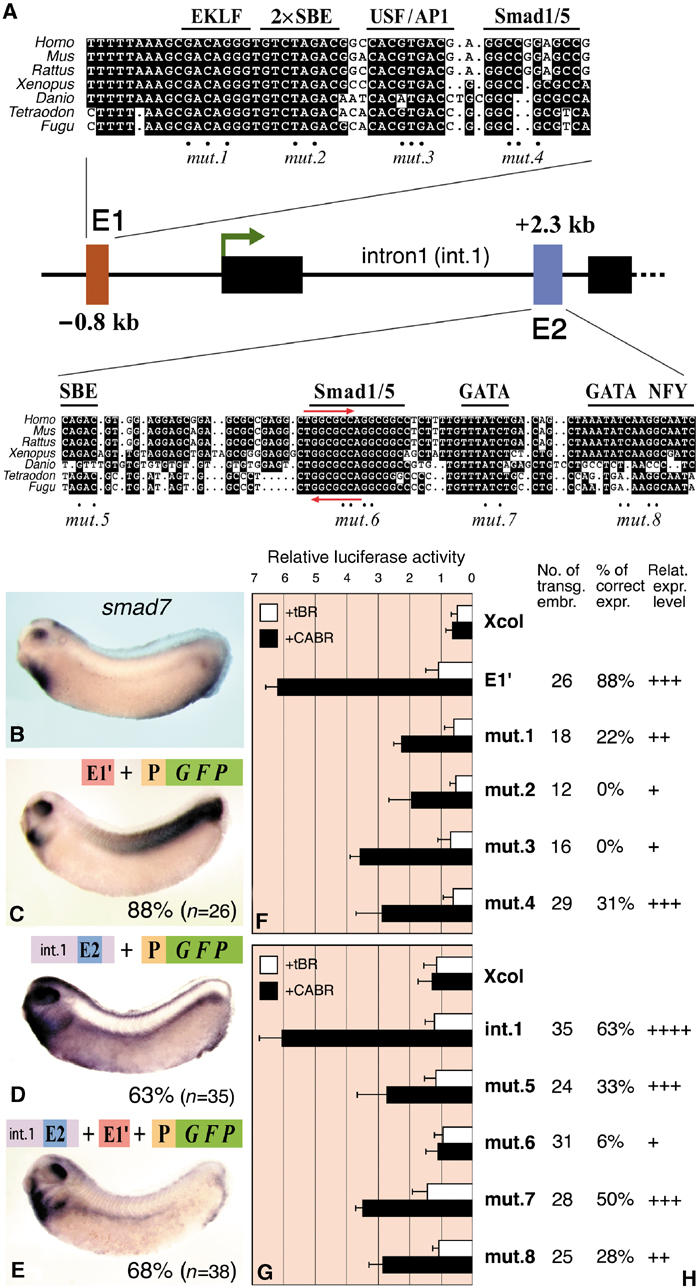
Characterization of the BREs of smad7. (A) Map of the Xenopus smad7 gene with the phylogenetically conserved putative enhancers E1 and E2. Multi-species sequence alignment with putative TF binding sites is shown for each enhancer. Red arrows in E2 indicate the bre7 motif also found in the bambi enhancer. Mutated nucleotides are indicated with dots. For transgenic and luciferase reporter assays, E1 was cloned with 24 bp upstream and 58 bp downstream nonconserved flanking sequences (E1′). (B) In situ hybridization of smad7 mRNA at the tailbud stage. (C–E) gfp in situ hybridization of transgenic embryos with the depicted constructs. P is the minimal promoter of bambi (−154/+60). The percentage of embryos with the depicted expression pattern is shown. (F, G) Data from luciferase reporter assays of the smad7 enhancers. E1′, intron1 or their mutated versions (see panel A) were cloned upstream of the Xcol minimal promoter and injected in embryos together with tBR or CABR mRNA as indicated. (H) Tabular results of embryos transgenic for the intact or mutated constructs (see panel A). The pattern referred to as correct is the one depicted in panel C (for E1′) and D (for intron1). The number of transgenic embryos analyzed, the percentage of embryos with correct pattern and the relative strength of transgene expression for each construct are shown.
