Figure 4.
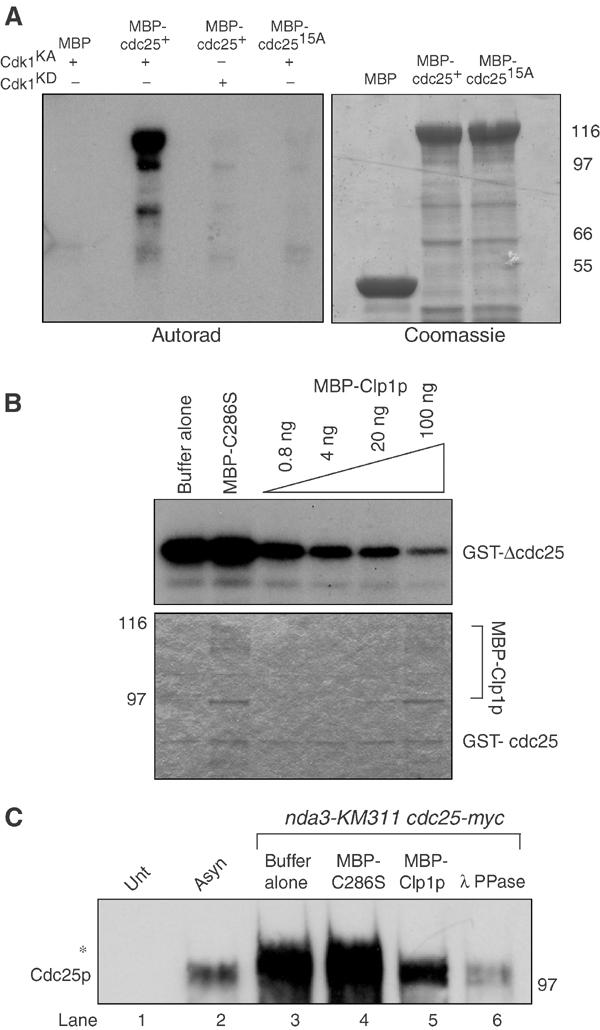
Clp1p reverses Cdk1p-dependent phosphorylation of Cdc25p. (A) Approximately 1–2 μg of MBP, MBP-Cdc25p, or MBP-Cdc25p-15A was phosphorylated in vitro with baculoviral produced and purified recombinant active (KA) or kinase dead (KD) Cdk1p complex. Reactions were separated by SDS–PAGE and analyzed by Coomassie blue staining and autoradiography. (B) Approximately 100 ng of GST-ΔCdc25p containing amino acids 1–197 was phosphorylated by recombinant Cdk1p complex in vitro as in (A), and subsequently incubated with the indicated amounts of MBP-C286S or MBP-Clp1p. Reactions were separated by SDS–PAGE, and analyzed by Coomassie blue staining (lower panel) and autoradiography (upper panel). (C) Cell pellets from nda3KM311 cdc25-myc (KGY 3916) arrested at the restrictive temperature (18°C), and wild type (KGY 246) (Unt) and cdc25-myc (KGY 3377) (Asyn) grown to mid-log phase were collected. Extracts were prepared and immunoprecipitated with 9E10 antibodies and subsequently incubated with phosphatase buffer alone (lanes 1, 2, and 3), 100 ng MBP-C286S (lane 4), 100 ng MBP-Clp1p (lane 5), or 0.5 μg Lambda phosphatase (lane 6). Reactions were separated by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-Cdc25p antibodies. The asterisk (*) indicates the position of the hyperphosphorylated Cdc25p.
