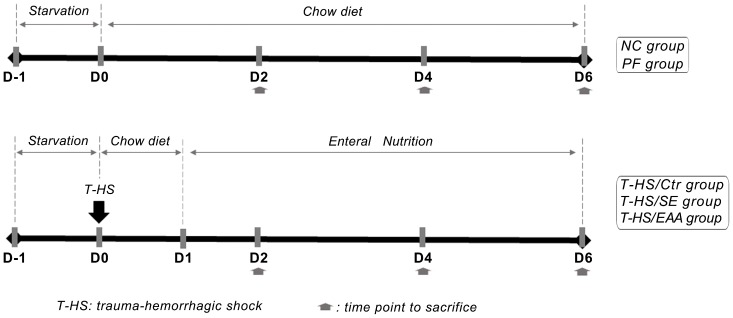
Figure 1. Experimental design.
This study includes five groups. After undergoing the trauma-hemorrhagic shock (T-HS) operation, rats received either standard enteral nutrition (EN) (T-HS/SE), essential amino acid (EAA) enriched high-protein EN (T-HS/EAA), or a continue infusion of isotonic saline but on normal chow diet (T-HS/Ctr). Food intake in a pair-fed group (PF) was restricted to the T-HS/Ctr group. A normal control group (NC) without T-HS and fed ad libitum chow was also included. Six individuals in each group were harvested on days 2, 4, and 6, respectively.