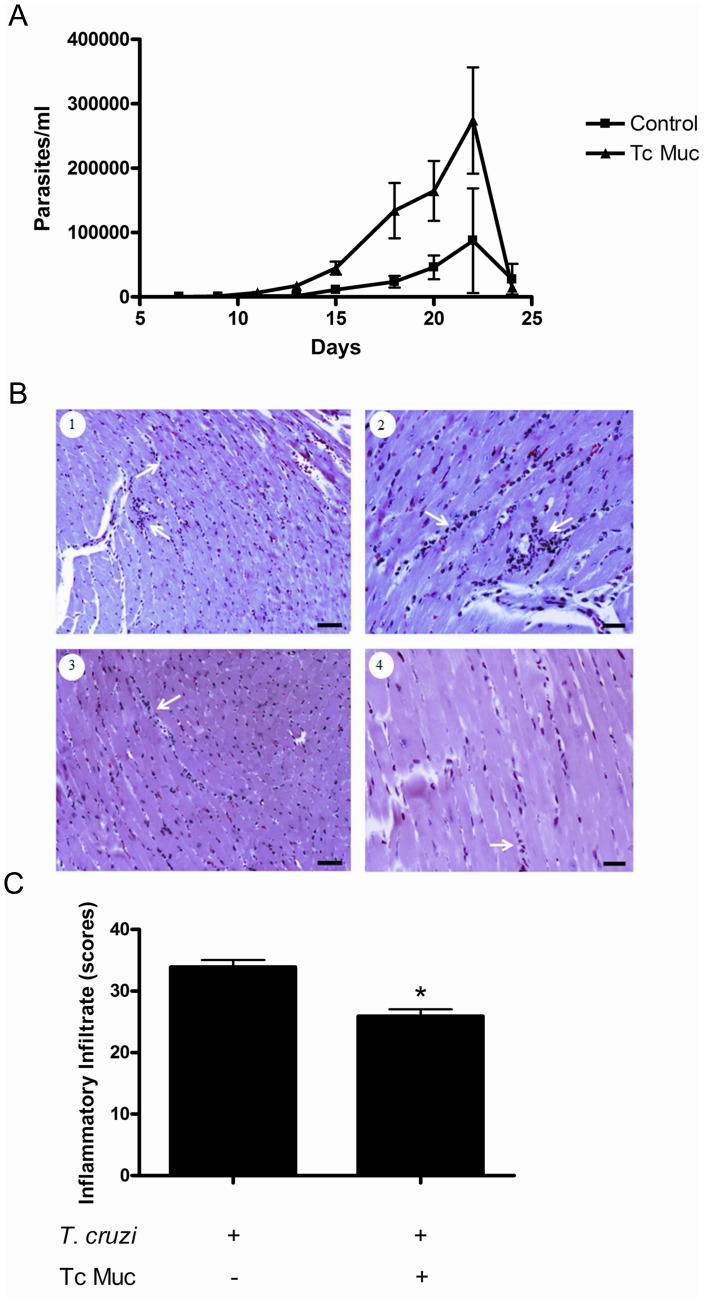
Figure 7. T. cruzi infected mice develop a higher parasitemia and reduced heart inflammatory infiltration when treated with Tc Muc.
BALB/c mice were infected via i.p. with 2×105 chemically induced metacyclic forms of Trypanosoma cruzi Dm28c clone. The mice received i.p. injections of Tc Muc (20 µg/mouse) or PBS on alternate days starting at day of infection. (A) The parasitemia for each mouse group was represented as the mean ± the standard deviation (SD) (n = 5). The parasitemia of mice from the Tc Muc treated group was significantly higther than untreated control mice (P≤0.01). (B and C) Inflammatory infiltration is diminished in the heart by treatment with Tc Muc. Twenty four days after infection cardiac fragments were extracted from Trypanozoma cruzi infected mice (B, 1–2) untreated or (B, 3–4) treated with Tc Muc. Slides were stained with haematoxylin-eosin and cellular nuclei from inflammatory and resident cells counted using Leica QWin program in sections with different magnifications, 40× (B, left panels) and 100× (B, right panels). (C) Inflammatory indexes were determined by counting inflammatory foci (average counts per field). Data were obtained from survivors (2 independent experiments) and shown as mean/standard error of the mean. Asterisk (P≤0.05) means statistical difference between infected mice treated with Tc mucin versus infection control group.