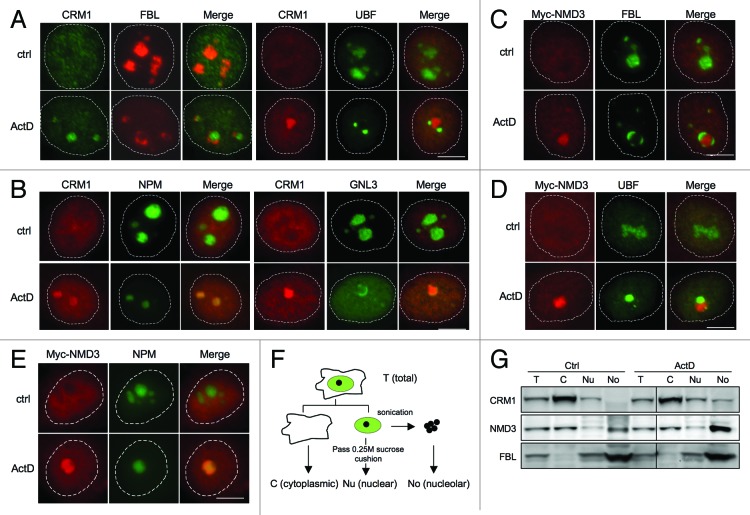
Figure 1. CRM1 and Myc-NMD3 accumulate in the nucleolus. (A) HeLa cells were treated with ActD (50 ng/ml) for 3 h as indicated. The cells were co-stained for FBL and CRM1 or for UBF and CRM1 as shown. (B) Cells expressing NPM-ECGFP were treated with ActD followed by staining for CRM1, or HeLa cells were treated with ActD followed by co-staining for GNL3 and CRM1. (C and D) HeLa cells transfected with Myc-NMD3 expression vector were treated as in (A) and co-stained for Myc-NMD3 and FBL (C) or Myc-NMD3 and UBF (D). (E) HeLa cells stably expressing NPM-ECGFP were transfected with Myc-NMD3, treated as in (A) and stained for Myc-NMD3. Scale bars, 10 µm. (F) Protocol of cellular fractionation to purify cytoplasmic, C; nuclear, Nu and nucleolar, No fractions. Note that the nuclear fraction contains also the nucleoli. T denotes total cellular extract. (G) Cells were treated with Act D (50 ng/ml) for 3 h followed by fractionation according to the scheme in (F), followed by western blot analysis for CRM1 and NMD3. Forty micrograms of protein from each fraction was loaded. FBL was used as a nucleolar marker.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.