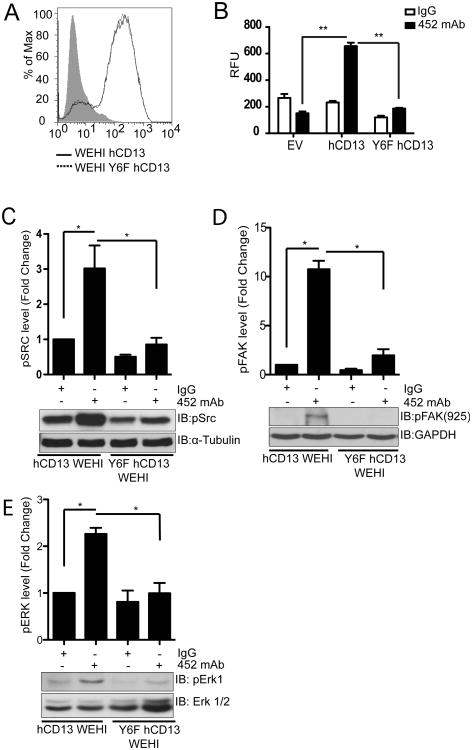
Figure 5. Mutation of the CD13 cytoplasmic tail attenuates crosslinking-induced monocyte adhesion and signaling.
A) WEHI 78/24 mouse monocytic cells stably expressing human CD13 (hCD13) or human CD13 with tyrosine6 mutated to phenylalanine (Y6F) were analyzed for hCD13 expression by flow cytometry. B) Calcein labeled empty vector (EV) or hCD13 or Y6F hCD13 expressing cells were treated with control IgG or activating 452 mAb (5.0 μg/mL) for 30 min, washed, allowed to adhere to human CD13 expressing monolayer cells for 30 min, lysed and fluorescence read at 485/530 nm. **; p<0.01. C-E) hCD13 or Y6F hCD13 expressing WEHI cells were treated with IgG or 452 mAb for 30 min. and analyzed by western blot using C) anti-phospho-Src, D) anti phospho-FAK Tyr925 and E) anti-phospho ERK1. Data combine 3 separate experiments.