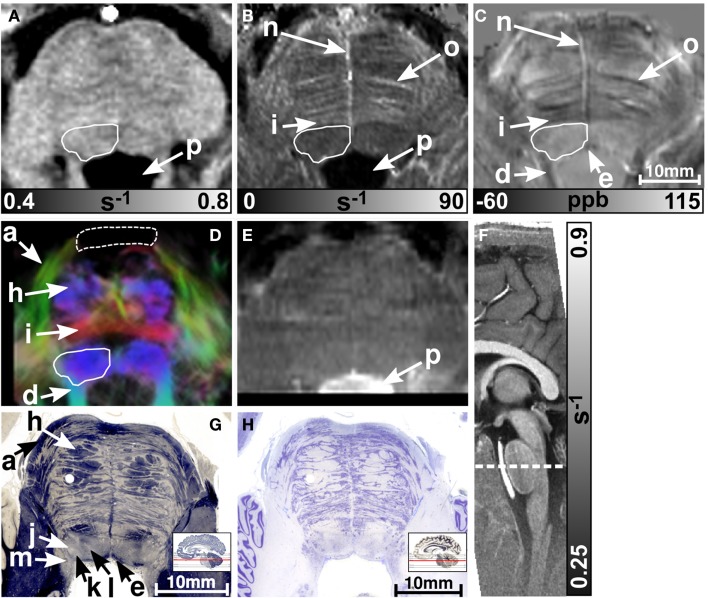
Figure 4.
Images of the middle part of the pons. R1, , and susceptibility maps as well as track-density (same color-encoding as in Figure 1; slightly distorted compared to the other axial image contrasts) and T2-weighted images of the same region are presented in axial orientation from (A–E), respectively. The sectional plane of the axial images is indicated by the dashed line overlaid on the sagittal R1 map shown in (F). Axial histological sections from a different subject stained for myelin and cells are illustrated in (G) and (H), respectively. The arrows in the images indicate: (a) middle cerebellar peduncle, (d) superior cerebellar peduncle, (e) medial longitudinal fasciculus, (h) corticospinal fibers, (i) pontocerebellar tract, (j) facial nucleus, (k) salivatory nucleus, (l) abducens nucleus, (m) solitary nucleus, (n) vein, (o) fiber bundle that traverses the pons in medial to lateral direction, and (p) fourth ventricle (cerebrospinal fluid). The solid white outline in (A–D) summarizes the caudal part of the pontine reticular nucleus, the facial nucleus, salivatory nucleus, and abducens nucleus. The dashed white outline in (D) indicates a region between the middle cerebellar peduncle that could not be resolved with TDI. [The histological stains (G,H) were adapted with permission from http://www.brains.rad.msu.edu and http://brainmuseum.org, supported by the US National Science Foundation.]