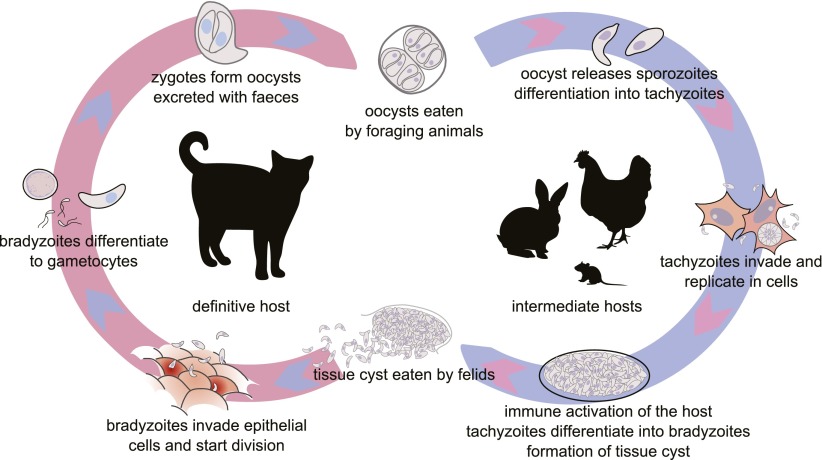
Figure 1. The life cycle of T. gondii.
All warm blooded animals may serve as intermediate hosts, which are infected by ingestion of food or water contaminated by oocysts. Felids, the definitive hosts, are infected by ingesting tissue cysts from their prey. The intermediate phase of the life cycle may be prolonged by carnivory between intermediate hosts (not shown). Modified from free-license pictures.