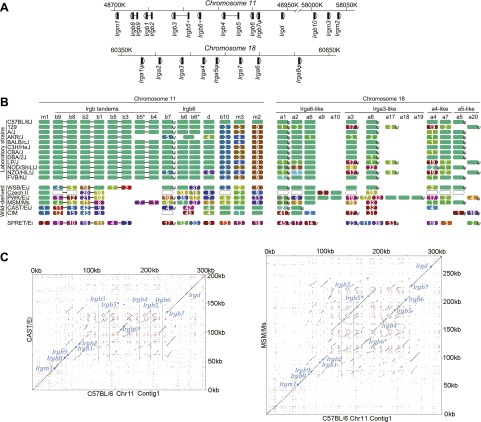
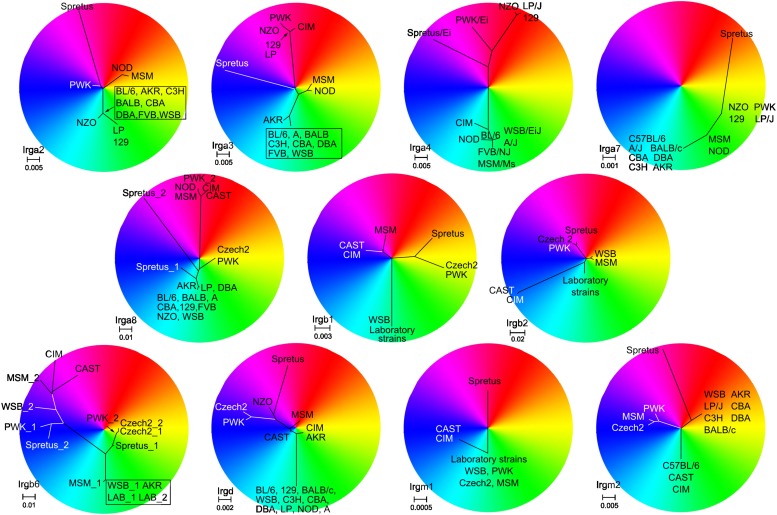
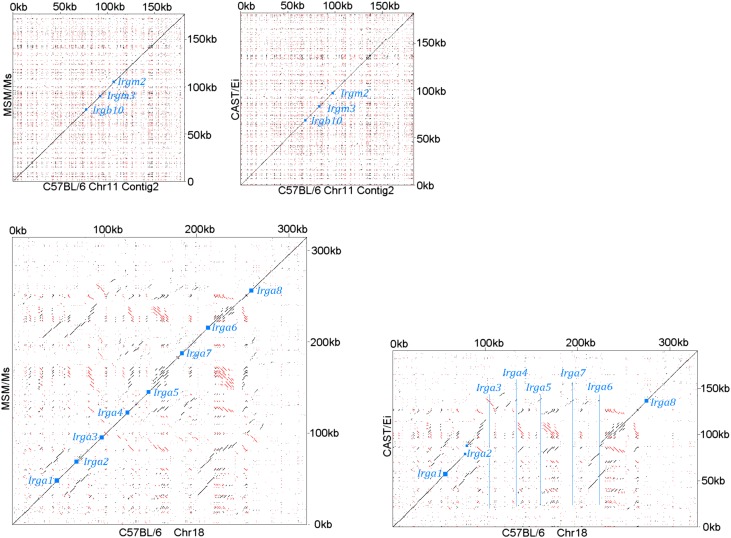
Figure 2. IRG protein polymorphism in inbred mouse strains.
(A) Linear order of IRG gene clusters on Chr 11 and Chr 18 of mouse strain BL/6. (B) Polymorphism at the protein level in the IRG genes of Chr 11 and Chr 18. Irga9–Irga20 are absent from BL/6 and are inferred from resequencing data. Each colour block represents one IRG open reading frame and shows the number of amino acid substitutions/indels relative to the BL/6 allele. The colours of the blocks indicate their phylogenetic relationship (Figure 2—figure supplement 1). Open blocks in strains Czech II and CIM indicate homologues expected but not yet found. ‘ψ’ indicates probable pseudogenes. (C) Dot plots of the longer IRG gene clusters on Chr 11 in CAST/Ei and MSM/Ms against the BL/6 genomic sequence. Small blue squares show the positions of homologous coding units, blue lines indicate the positions of genes in BL/6 that are absent from the other genomes.