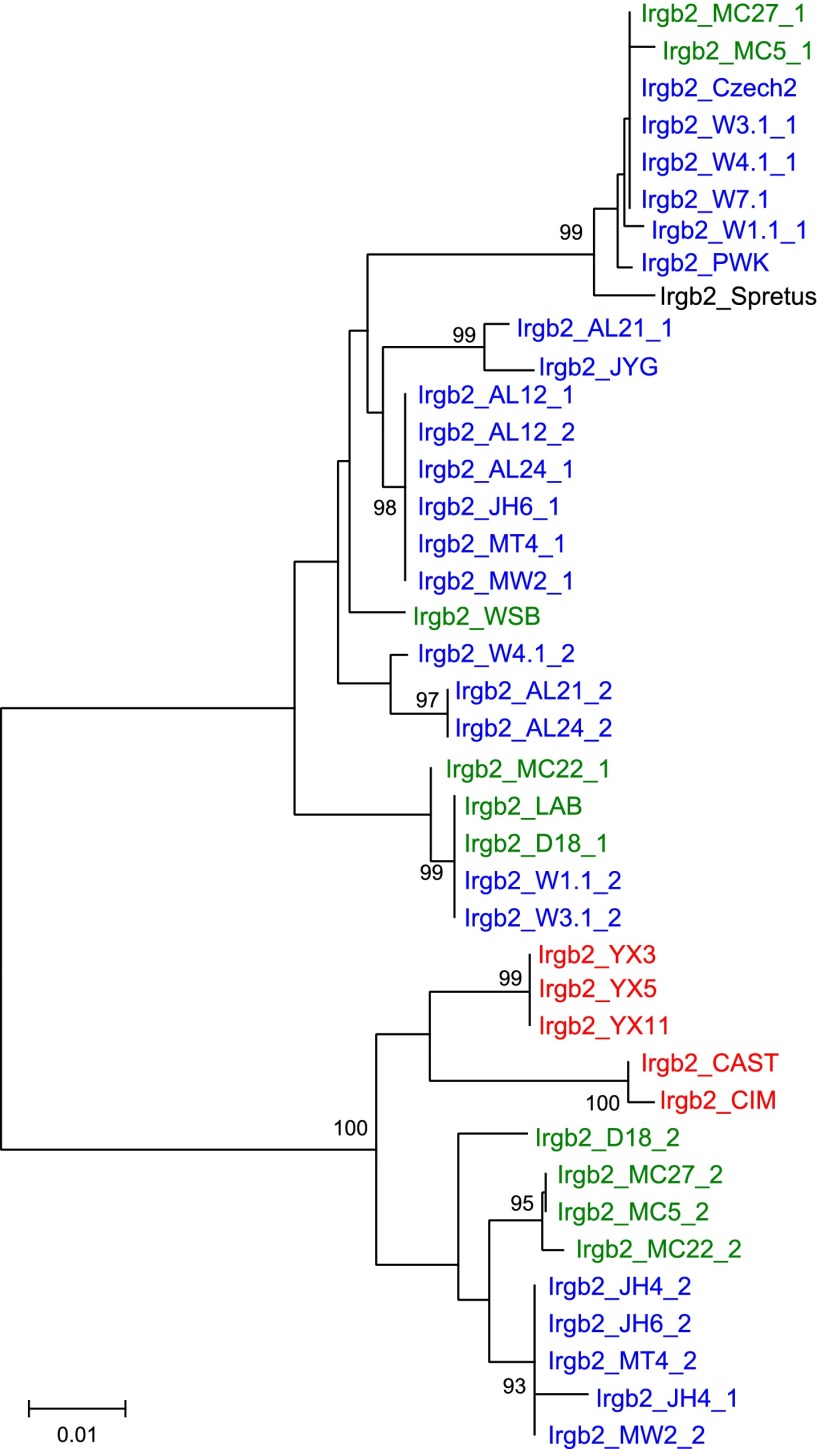
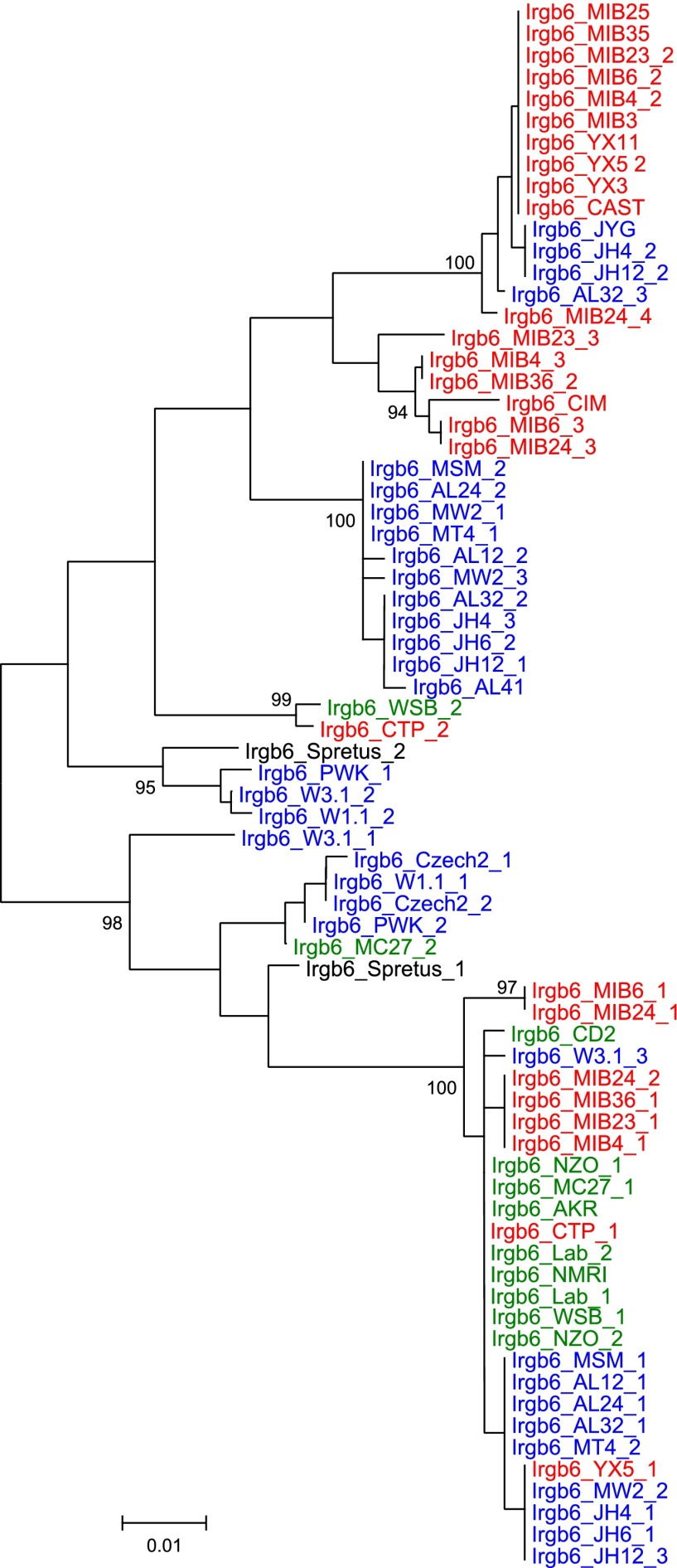
Figure 3. Polymorphism of five IRG genes.
(A) Phylogenetic trees of five IRG genes sequenced from DNA of wild mice collected from various sites in Eurasia. Green, blue and red taxa represent M. m. domesticus, M. m. musculus and M. m. castaneus samples respectively. The black taxon represents Mus spretus. Alleles found in heterozygous condition in certain mice are indicated by numbers appended to individual mouse identifiers (some haplotypes contain 2 Irgb6 paralogous genes (Figure 2B), hence potentially up to 4 alleles). Bootstrap values are shown if >90. The sequences are avaliable in (Figure 3—source data 2-6). (B) The nucleotide pairwise diversities (π) of genes across seven laboratory and wild-derived inbred mouse strains (BL/6, AKR/J, MSM/Ms, CAST/Ei, PWK/PhJ, WSB/Ei and Spretus/EiJ). Grey bars indicate the distribution of π from 50 ‘random’ genes (Figure 3—source data 1). The π values of individual IRG and MHC genes are indicated by arrows.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.01298.007
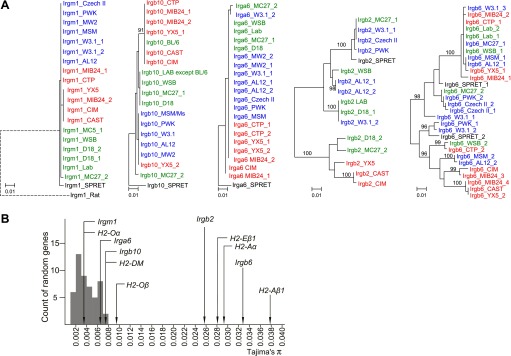
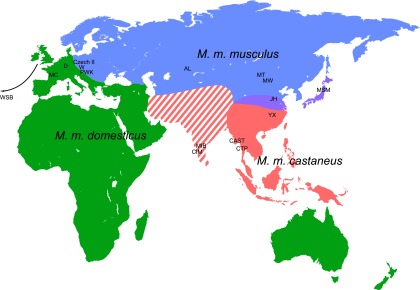
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. Mouse samples collected for this study.