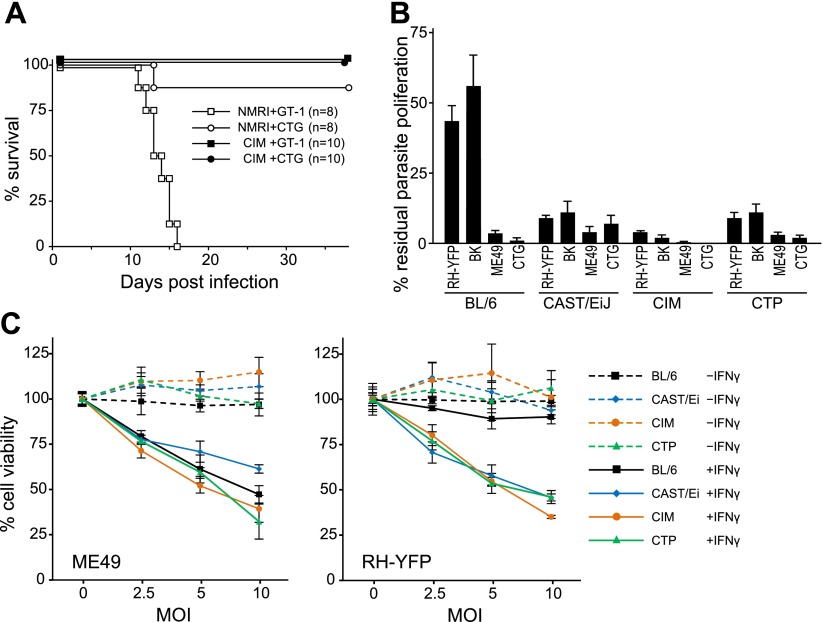
Figure 4. Resistance of wild-derived mouse strains to virulent T. gondii.
(A) Cumulative mortality of NMRI and CIM mice infected with 100 or 300 (data pooled) tachyzoites of the indicated T. gondii strains. (B) IFNγ-mediated growth inhibition of virulent (type I RH-YFP, BK) and avirulent (type II ME49, type III CTG) T. gondii strains in DDC of laboratory (BL/6) and wild-derived, inbred mice (CAST/Ei, CIM, CTP). Proliferation of parasites was measured by 3H-uracil incorporation and is displayed as percentage of residual T. gondii proliferation, as described in ‘Materials and methods’. Error bars show standard deviations of quadruplicate values. (C) IFNγ-dependent reactive cell death of mouse DDC cell lines infected with T. gondii. DDC were either stimulated with 100 U/ml of IFNγ 24 hr prior to infection or left unstimulated. Cells were infected with type II strain ME49 or type I strain RH-YFP at the indicated MOIs for 8 hr. Cell viabilities were measured as described in ‘Materials and methods’ and expressed as percentages of those recorded for uninfected cells (MOI = 0). Error bars show standard deviations of quadruplicate values.