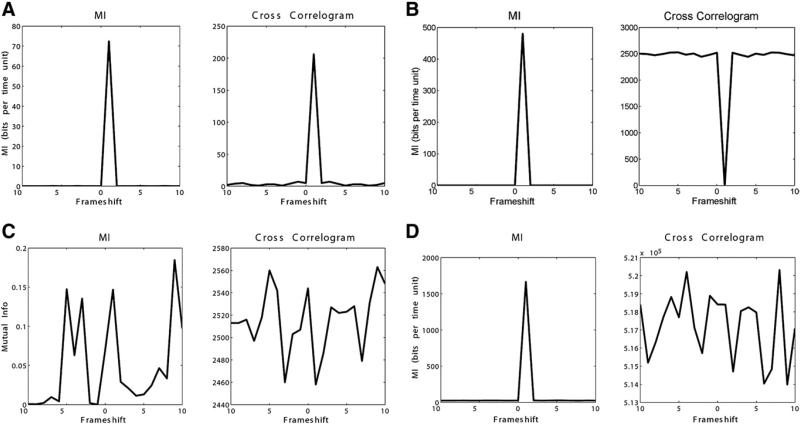
Figure 3.
(A) Simulation of positively correlated data with frameshift of 1. Concordant peaks seen in time-delayed mutual information (MI) and cross-correlation at the correct frameshift. (B) Simulation of negatively correlated data with frameshift of 1. Peak seen in time-delayed MI and trough seen in cross-correlation at the correct frameshift. (C) Simulation of two independent (no relationship) spike trains evaluated using time-delayed MI and cross-correlation. (D) Mapping (substitution cipher) function between two spike trains with frameshift of 1. Four-bit words in one spike train are directly mapped to four-bit words in another spike train. Peak seen in time-delayed MI at the correct frameshift, and erratic behavior in cross-correlation. Map used was 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 map to 5, 10, 14, 1, 8, 2, 2, 15, 9, 2, 4, 8, 10, 11, 5, 6, respectively.