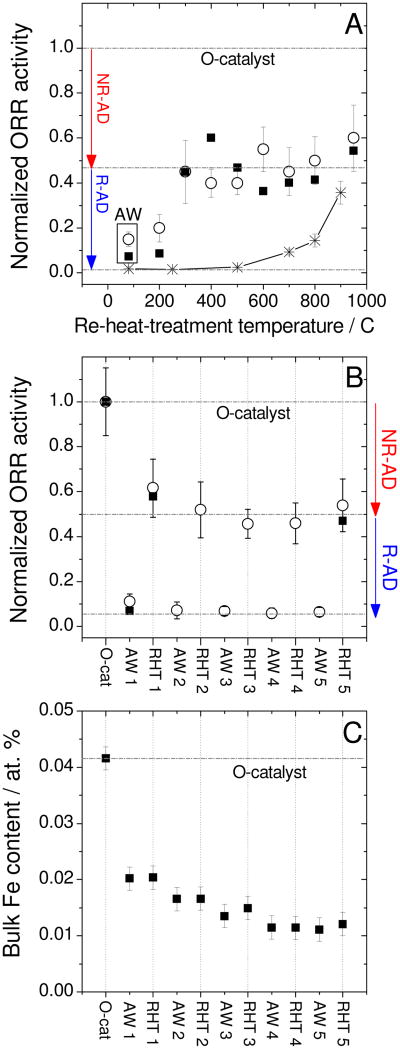
Figure 3. Activity recovery by re-heat-treatment in argon of acid-washed catalysts.
(A) Normalized activity based on that of the original catalyst (O-catalyst) vs. re-heat-treatment temperature in argon, as measured in RDE (open circles) and PEMFC (filled squares).
The acid-washing was performed in a pH 1 H2SO4-solution for 24 h, then the powder was filtered, rinsed with deionized water and dried. Several aliquots of the acid-washed catalyst (AW-catalyst) were re-heat-treated in argon at various temperatures for 1 h. The initial activities of the O-catalyst were 2.8 and 15.1 A g-1 in RDE and PEMFC, respectively. Aliquots of a test precursor initially free of active sites (see section 2.1.4) were heat-treated in argon at various temperatures for 1 h (asterisks) in order to determine the minimum temperature required for catalytic-site formation.
(B) Normalized activity as measured in RDE (open circles) or PEMFC (filled squares) at various steps of five successive acid-washing/re-heat-treatment cycles. Acid-washed and re-heat-treated catalysts are labeled AWX and RHTX, respectively, X denoting the cycle number. Each acid-washing lasted 24 h in a pH 1 H2SO4-solution, then the powder was filtered, rinsed and dried. Each AW-catalyst was re-heat-treated for 1 h at 950°C in argon.
(C) Bulk Fe content at each step of the five acid-washing/re-heat-treatment cycles described in (B), as measured by neutron activation analysis.