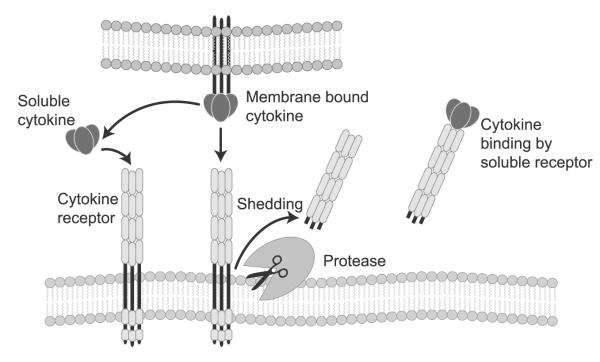
Fig. 1.
The biology of cytokines and cytokine receptors. Pro-inflammatory cytokines are released by nucleated cell types residing in the heart, including cardiac myocytes. Cytokines exert their biological effects by binding to cognate cytokine receptors on cell membranes (left side of the diagram). Cytokine receptors can be proteolytically cleaved or “shed” from cell membranes, which releases the soluble extracellular ectodomain of the cytokine receptor into the extracellular space and/or circulation (middle of the diagram). Cytokine receptors retain their ability to bind cytokine and to inhibit the biological activities of cytokines by preventing cytokines from binding to cognate receptors on target cells (right side of the diagram)