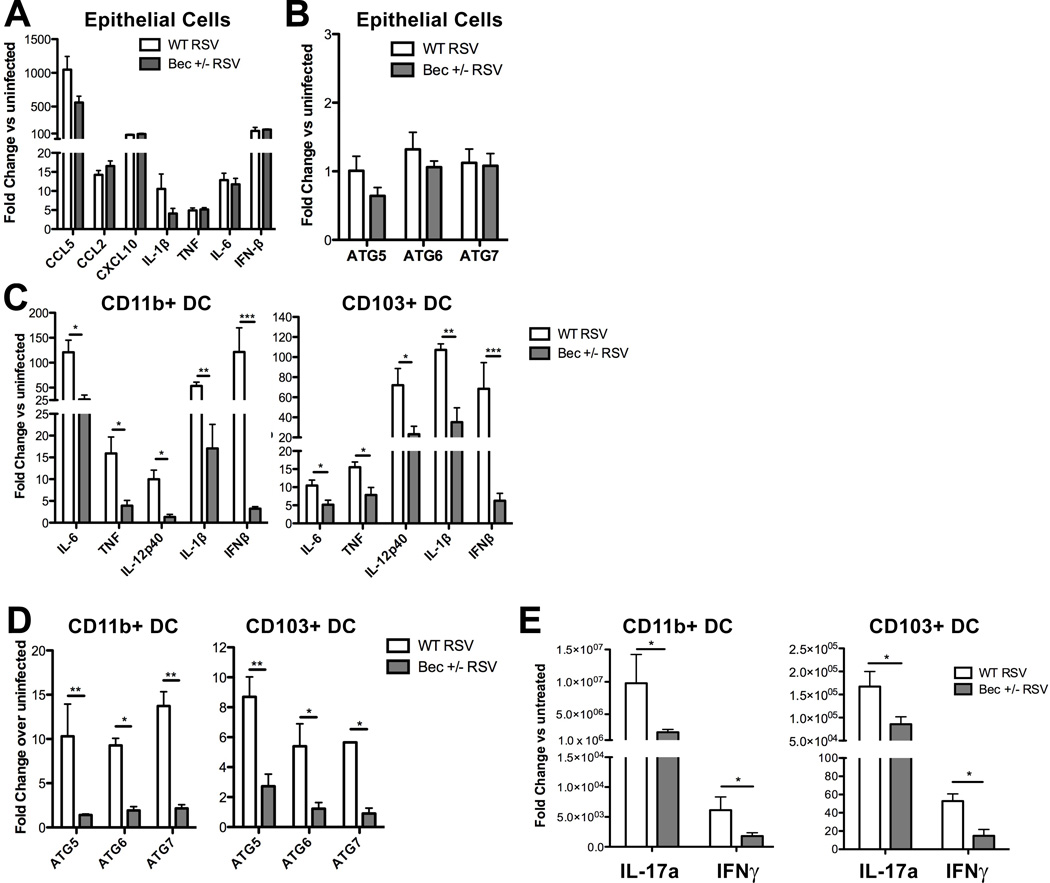
Fig. 3. Beclin-1+/− lung epithelial cells are competent in innate cytokine responses to RSV infection, while pulmonary DCs are impaired in innate cytokine production, autophagy gene expression, and antigen presentation upon RSV infection.
(A) Cytokine production and (B) autophagy gene expression by Beclin-1+/− or wild-type mouse primary alveolar epithelial cells was assessed by qPCR 24 hours post-RSV infection. (C–E) Pulmonary DCs were fluorescently labeled and flow-sorted from collagenase-digested lungs of naïve Beclin-1+/− or wild-type mice (see Supp. Fig. S1 for gating strategy), and infected with RSV at 1 DC: 1 pfu (1:1 MOI). Innate cytokine production and autophagy gene expression by CD11b+ lung DCs or CD103+ DCs (C) was assessed at 24 hours post-RSV infection by qPCR. Autophagy gene expression by CD11b+ DCs or CD103+ DCs (D) was measured by qPCR at 24 hours post-infection. Cytokine production by purified splenic CD4+ OT-II T cells, co-cultured with CD11b+ lung DCs or CD103+ DCs (E) treated concurrently with RSV and 200µg/ml whole ovalbumin protein, was assessed by qPCR at 24 hours. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments, with at least four replicates per group. Error bars represent SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.