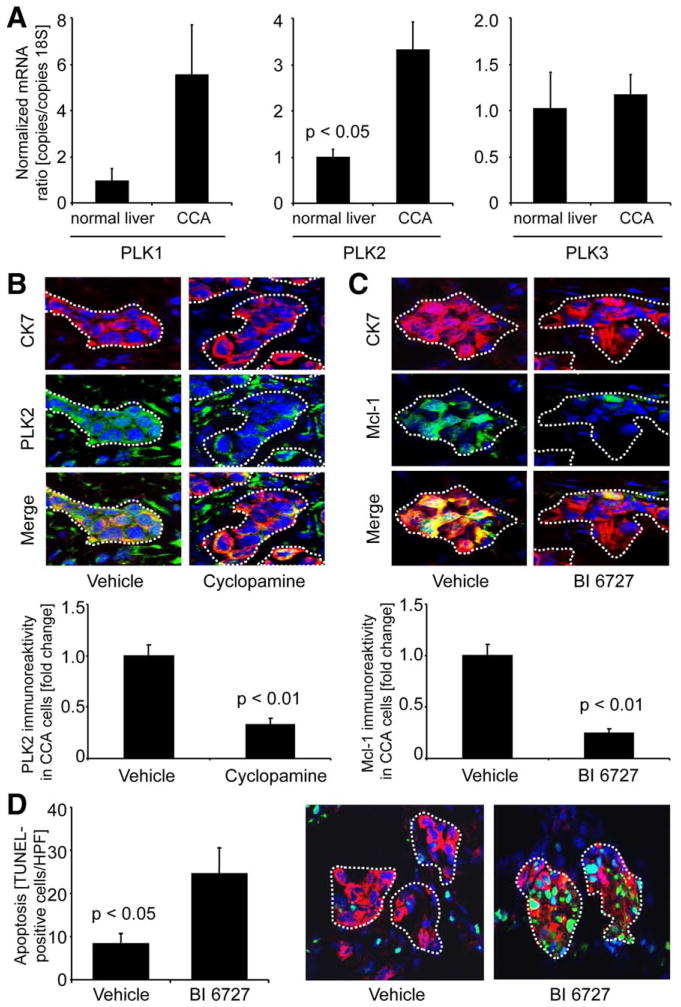
Fig. 6.
Effects of Hh and PLK inhibition are recapitulated in vivo. A syngeneic rat orthotopic CCA model (BDEneu cells; Fischer 344 rats) was employed for this study. (A) CCA and normal liver specimens of untreated rats were analyzed for mRNA expression of PLK1 (left), PLK2 (middle), and PLK3 (right) by quantitative RT-PCR. Mean±SEM; n=3. (B) CCA specimens of cyclopamine-treated (2.5 mg/kg b.w. IP daily for 1 week; first injection: postoperative day 7; seventh injection: postoperative day 13) or vehicle-treated rats were analyzed for PLK2 (green) expression of tumor cells (identified by costaining for CCA cell marker CK-7; red) by IF microscopy. Merged images depict colocalized CK-7/PLK2 protein expression in yellow (green-red overlay). PLK2 immunoreactivity in CCA cells was quantitated using the software, ImageJ 1.44o (B lower; mean±SEM, n=7). (C) CCA specimens of BI 6727-treated (3 injections of 10 mg/kg b.w. IP every other day; first injection: postoperative day 7; third injection: postoperative day 11) or vehicle-treated rats were analyzed for Mcl-1 (green) expression of CCA cells (similar CK-7 costaining and quantitation [mean±SEM; n=9] as in B). (D) Apoptotic nuclei were assessed in CCA samples of vehicle-treated (left photomicrograph) and BI 6727-treated (right photomicrograph) rats by TUNEL staining (green), and the identity of TUNEL-positive cells was confirmed by CK-7 costaining (red). Quantitation of TUNEL-positive cells (expressed as number per high power field [HPF], D left) demonstrates that in BI 6727-treated animals, CCA cell apoptosis was increased, as compared to controls (mean±SEM; n=9). In all photomicrographs, nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue) and CCA glands within the tumor stroma are illustrated by white dotted lines.