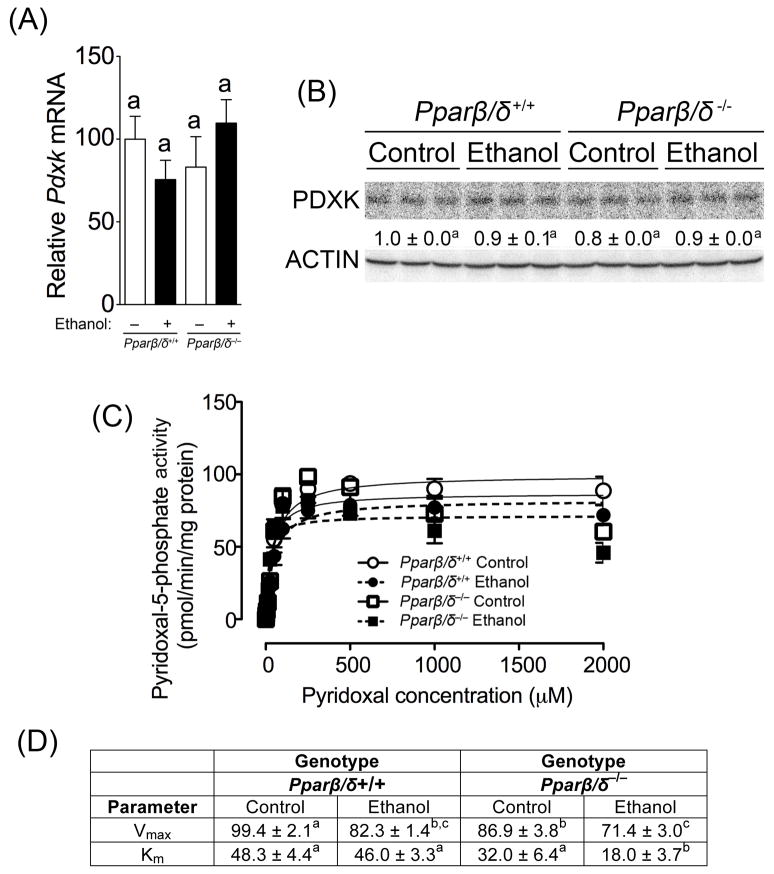
Fig. 7.
Ethanol decreases PDXK Vmax and causes a PPARβ/δ-dependent maintenance of PDXK Km. (A) Relative hepatic mRNA expression of Pdxk in liver of control or ethanol-fed wild-type (Pparβ/δ+/+) and Pparβ/δ-null (Pparβ/δ−/−) mice after four months. (B) Western blot analysis of PDXK in the liver of control and ethanol-fed Pparβ/δ+/+ and Pparβ/δ−/− mice after 4 months. (C) Michaelis-Menten kinetic parameters were derived from the enzyme assay for PDXK activity using liver enzyme extracts from control and ethanol-fed Pparβ/δ+/+ and Pparβ/δ−/− mice after 4 months. (D) Vmax and Km values calculated from the enzyme assay for PDXK activity using liver enzyme extracts from control and ethanol-fed Pparβ/δ+/+ and Pparβ/δ−/− mice after 4 months. Values represent the mean ± S.E.M.. Values with different letters or superscripts are significantly different at P ≤0.05.