Figure 2.
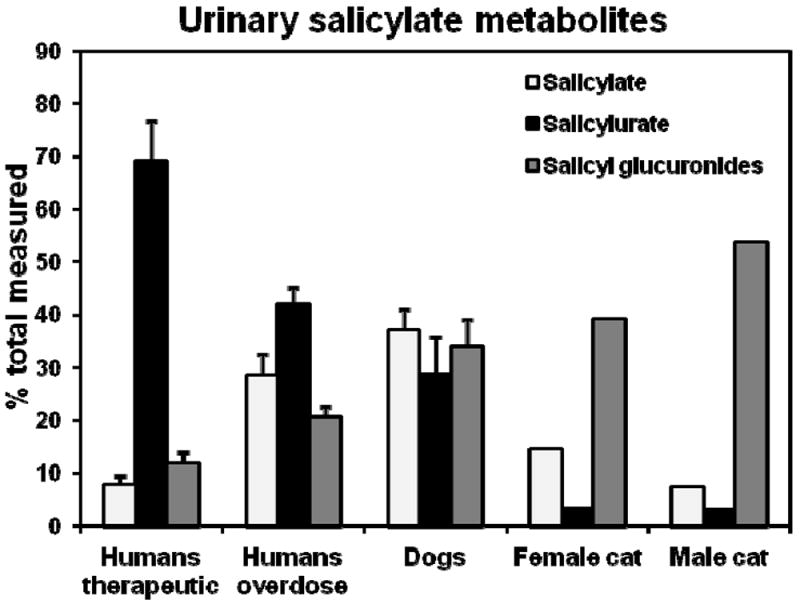
Cats can readily glucuronidate salicylate, but they poorly conjugate salicylate with glycine (forming salicylurate). Shown are data from several studies comparing the urinary metabolites of salicylate when administered as the sodium salt to 7 dogs and 2 cats (one male, one female) at 44 mg / kg intravenously, or orally as acetylsalicylic acid to 25 human volunteers at a therapeutic dose of 650 mg, or to 24 human patients that had intentionally taken a moderate aspirin overdose. Data are from Davis et al (1972) for cat and dog, Chen et al (2007) for human volunteers, and Patel et al (1990) for overdose patients.
