Figure 4.
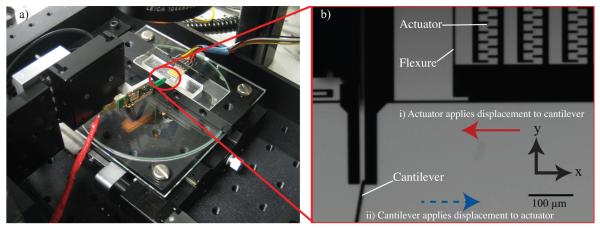
(a) Experimental setup for calibration of the electrostatic actuator. (b) Magnified image highlights details of calibration with piezoresistive cantilever. (i) Voltage is applied to the device to displace actuator in the direction of the solid red arrow while the cantilever is held stationary. The deflection signal of the piezoresistive cantilever indicates force-voltage relationship of ASC is β = 0.019 μN/V2. (ii) To measure the passive spring stiffness of the device (kspring), the linear actuator moves the cantilever in the direction of the blue dotted arrow while the device is held stationary on the stage. The device stiffness is extracted from these data, where kdevice = 0.54 N/m. The apparent cantilever stiffness caused by the 10° offset from the vertical orientation was accounted for as noted by Park et al [31].
