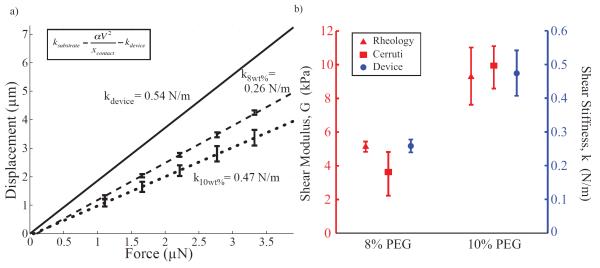
Figure 7.
Characterization of PEG hydrogels. (a) The ASC device is capable of determining the effective stiffness of various cross-linker concentrations of PEG gels. Optical observation of displacements under the microscope for various force loading conditions was used to calculate the effective stiffness of substrates. The solid black line the linear fit of the device displacement in the unloaded state. These results also show that k10wt% (dotted black line) has a higher effective stiffness than k8wt% (dashed black line) for PEG gels (0.47 ± 0.06 N/m and 0.26 ± 0.02 N/m respectively). Note that stiffer substrates result in less displacement. Error bars show standard deviation of empirical measurements at representative voltages across all samples tested (n = 5). (b) Comparison of shear moduli of 8 wt% and 10 wt% PEG gels based on empirical ASC data and rheological measurements. Rheology and obervations of displacements used for Cerruti’s formulation provide estimates of shear modulus (left axis, n = 3 samples), while the ASC provides shear stiffness (right axis, n = 5) confirmed to correlate appropriately with G through a computational model.