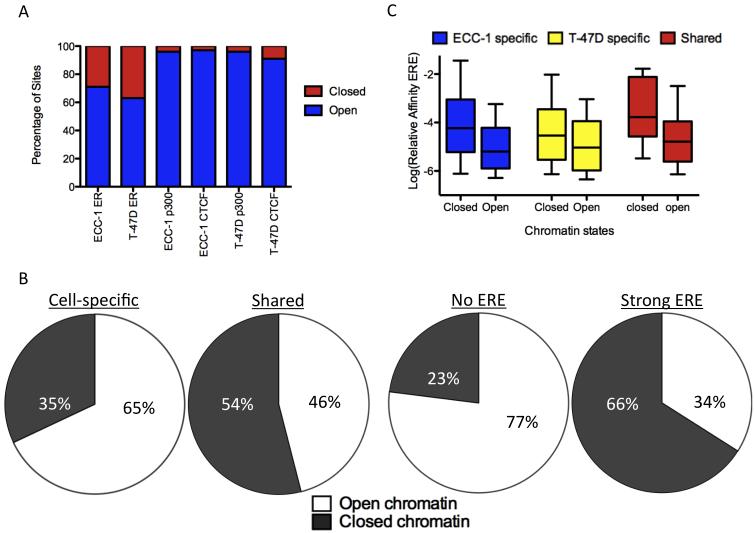
Figure 2. Relationship between chromatin accessibility and cell-specific binding.
A) DNaseI hypersensitivity data is comprehensive, capturing >90% of p300 and CTCF binding sites in each cell type, while indicating that ~65% of ER binding sites are found in open chromatin prior to treatment with E2. B) Most ER binding sites that are cell-specific and lack strong matches to an ERE are found in open chromatin prior to E2 treatment, while ER binding sites that are shared between the two cell lines and have strong EREs are found in closed chromatin prior to treatment. C) Bound EREs found in closed chromatin prior to E2 treatment are stronger matches to an ERE than sites found in open chromatin for ECC-1 specific (blue), T-47D specific (yellow) and shared (red) ER binding sites. See also Figure S2.