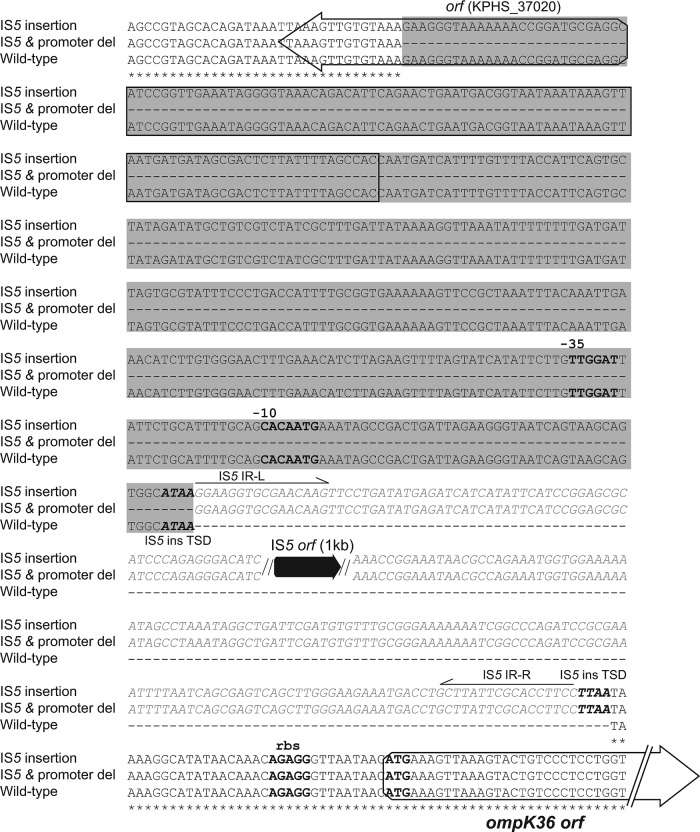
Fig 1.
Nucleotide sequences of the upstream regions of the ompK36 gene in strains with wild-type sequence, a full-length IS5 insertion, and an IS5 insertion along with a promoter deletion. Nucleotide positions shared by the three strains are marked with asterisks; missing bases are indicated by dashes. The ompK36 ribosome binding site (rbs), start codon, and −10 and −35 promoter sequences are shown in boldface, while the presumed IS5 element integration sites (target site duplications [TSD]) are shown in boldface italics. Open reading frames (ORFs) are portrayed by arrows, with the IS5 transposase ORF indicated in black and the upstream ORF (KPHS_37020) and ompK36 ORF in white. The inserted IS5 element, including the IS5 transposase ORF (black arrow) and its right and left inverted repeats (IR-R and IR-L), are shown in gray italic letters. Single-line arrows beneath the inverted repeats indicate the direction of the repeats. A 1,200-bp IS5 element is inserted 33 bp upstream of the ompK36 start code from the TSD site (TTAA), which qRT-PCR data indicate is disrupting the transcription of ompK36. The gray shading denotes a 395-bp deletion region, encompassing a partial sequence of an unknown ORF (KPHS_37020) and the −30 and −10 promoters. The IS5 insertion and promoter deletion also disrupt ompK36 expression.