Fig 6.
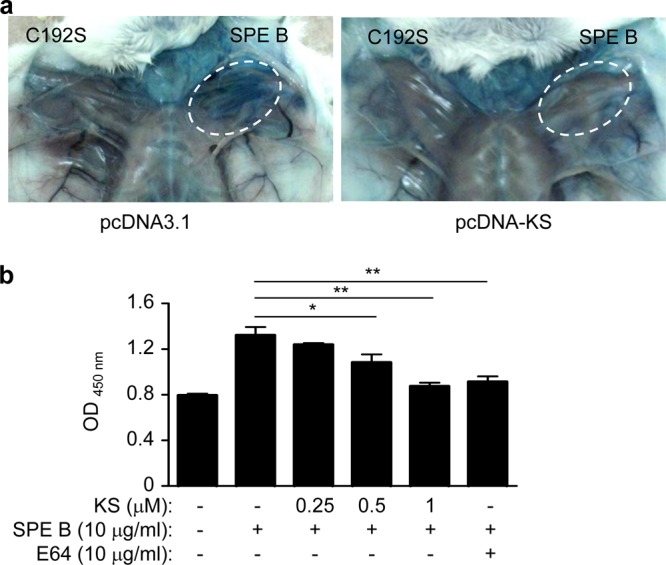
KS reduces vessel permeability induced by GAS virulence factor SPE B. (a) At 12 h after hydrodynamic administration of the KS plasmid or control plasmid, mice were subcutaneously injected with SPE B wild-type or C192S mutant protein without protease activity (25 μg in 50 μl PBS) for 1 h and then injected with Evans blue (10 mg/ml, 200 μl/mouse) through the tail vein. Mice were sacrificed after 30 min, and the local tissue was observed. (b) A monolayer of human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1) in a Transwell was pretreated with KS for 12 h, and the supernatant was placed in fresh medium with SPE B for 1 h. E64 (10 μg/ml), a cysteine protease inhibitor, was used to inhibit SPE B activity as a control. Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) was added in the upper well for 30 min, and the lower-well culture medium was collected to react with tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) substrate. The amount of penetrating HRP activity was measured with absorbance at 450 nm. Experiments were performed three times, and one representative experiment is shown. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.
