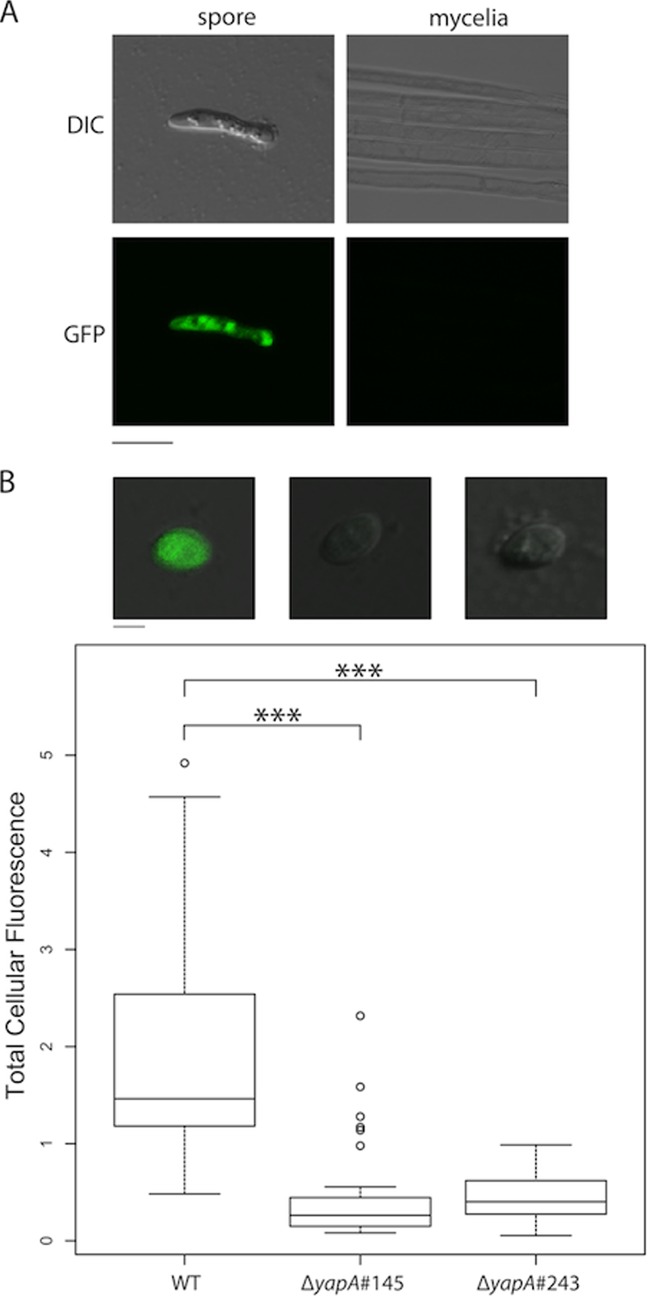
Fig 5.
Spore-specific expression of PcatA-eGFP. (A) Confocal and DIC microscopy images confirming the spore-specific expression of the PcatA-eGFP reporter, pGC13. Bar = 10 μm. (B) Spore-specific expression of the PcatA-eGFP-CL1 reporter, pGC14. The box plot shows the total amount of fluorescence per spore, indicating a significant decrease in EGFP fluorescence in ΔyapA spores relative to wild-type (WT) spores. Significance between samples was determined using Student's two-tailed t test: for the WT versus ΔyapA#145 strains, t100 = 9.6 and the P value was ≪0.0001 (***); for the WT versus ΔyapA#243 strains, t89 = 12.6 and the P value was ≪0.0001 (***); and for the ΔyapA#145 versus ΔyapA#243 strains, t34 = 0.3, and the difference was not significant. The total cellular fluorescence of each spore was quantified using ImageJ software. The image analysis was performed on maximum-intensity projection images that were generated from 5- by 1-μm confocal z stacks. Representative merged DIC and confocal fluorescence images showing EGFP expression in wild-type (WT), ΔyapA#145 (PN2740), and ΔyapA#243 (PN2739) spores are shown above the box plot. Bar = 2 μm. Multiple transformants, including Fl1::PcatA-eGFP-Cl1 (PN2838, PN2839, PN2840, and PN2841), ΔyapA#243::PcatA-eGFP-CL1 (PN2836, PN2837, and PN2844), and ΔyapA#145::PcatA-eGFP-CL1 (PN2842 and PN2843) transformants, were analyzed.