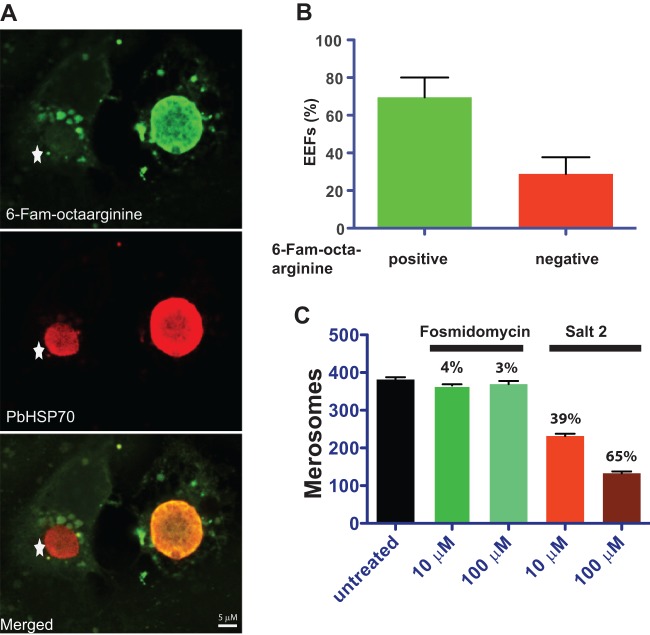
Fig 4.
Conjugation of fosmidomycin to octaarginine inhibits formation of Plasmodium berghei merosomes, the final stage of preerythrocytic development. (A) Fluorescence microscopy images of P. berghei-infected hepatoma cells. Incorporated FAM-octaarginine (green) and PbHSP70 (red) are shown. The exoerythrocytic form (EEF) on the left did not incorporate the FAM-octaarginine (star), whereas the EEF on the right did. (B) Quantification of P. berghei-infected hepatoma cells that incorporated FAM-octaarginine. Shown are mean values and standard deviations from three biological replicates. (C) Quantification of merosomes at 65 h after infection in the presence of either fosmidomycin or the fosmidomycin-octaarginine salt complex 2. Mean values with standard deviations from three independent replicates are shown. Numbers represent the percentage of inhibition of merosome formation compared to that of untreated samples.