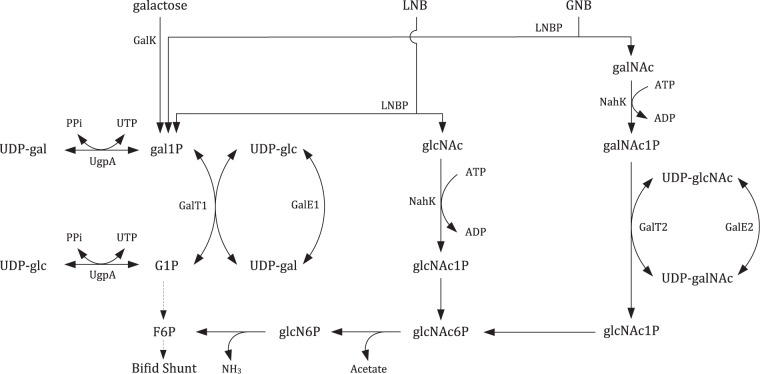
Fig 4.
Proposed routes for the breakdown of galactose, lacto-N-biose I (LNB), and galacto-N-biose (GNB) in B. bifidum. All 3 substrates yield gal1P, which is metabolized solely by the Leloir pathway (left). Depending on the presence of LNB or GNB, N-acetylglucosamine (glcNAc) or N-acetylgalactosamine (galNAc), respectively, is formed through the action of LNBP. Utilization of glcNAc requires only N-acetylhexosamine kinase (NahK) activity to generate glcNAc1P. However, GNB-rich substrates such as mucin need the full set of enzymes encoded by the GNB/LNB gene cluster (right). galNAc is phosphorylated to galNAc1P by NahK, which is subsequently converted by GalT2 and GalE2 via a Leloir-like pathway to glcNAc1P, which can then enter the bifid shunt via fructose 6-phosphate (F6P) by consequent action of a glucosamine mutase, a deacetylase, and a deaminase. glcN6P, glucosamine 6-phosphate.