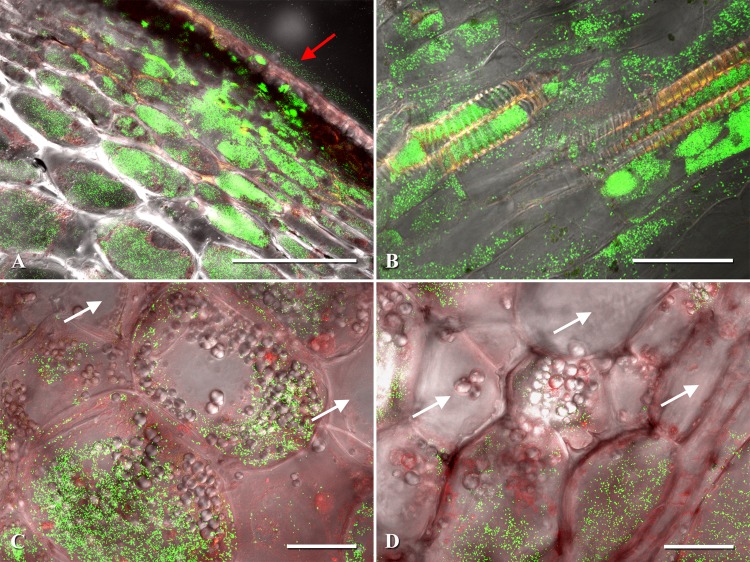
Fig 3.
Examples of Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. michiganensis-infected pericarp cells of tomato. (A) Pericarp lesion expansion with eGFP-labeled C. michiganensis subsp. michiganensis colonizing the exocarp and mesocarp. (B) Fruit xylem and xylem parenchyma colonization by C. michiganensis subsp. michiganensis. (C) Intracellular colonization of mesocarp cells by C. michiganensis subsp. michiganensis. (D) Intracellular colonization of the endocarp and surrounding parenchyma cells. Confocal microscopy images were generated by merging three channels (488 nm, 543 nm, and transmitted light). The red arrow points to the lesion on the fruit surface. White arrows indicate noncolonized fruit cells. Scale bars: 200 μm in panel A; 50 μm in panels B, C, and D.