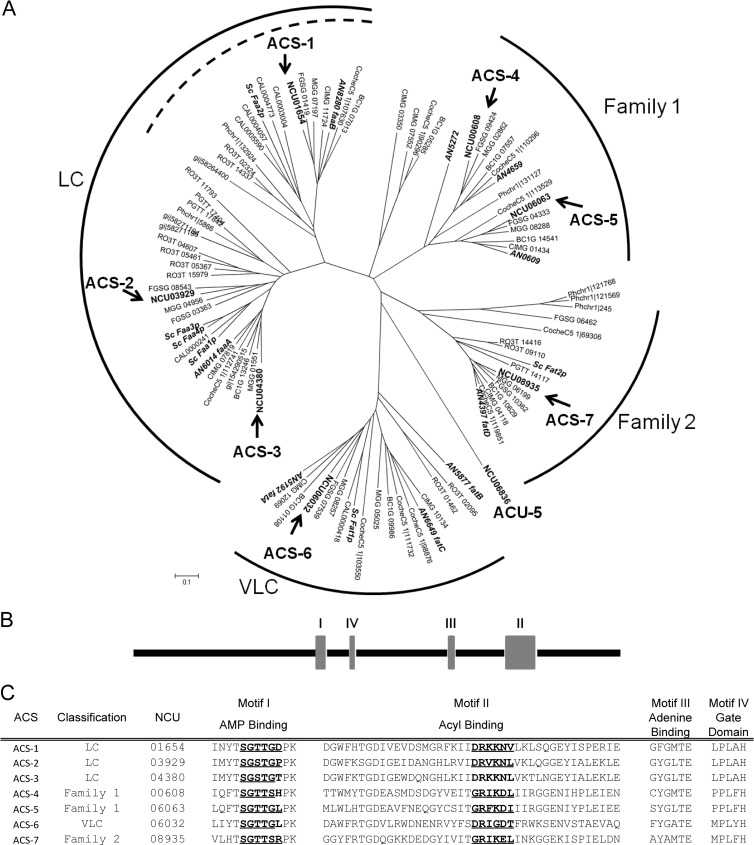
Fig 1.
Summary of acyl-CoA synthetases in fungi. (A) Phylogenetic tree of putative ACS proteins identified in 13 fungal species (Aspergillus nidulans, Botryotinia fuckeliana, Candida albicans, Cochliobolus heterostrophus, Coccidioides immitis, Cryptococcus neoformans, Fusarium graminearum, Magnaporthe grisea, Neurospora crassa, Phanerochaete chrysosporium, Puccinia graminis, Rhizopus oryzae, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae). N. crassa ACSs are in boldface, and gene names are indicated with arrows. A. nidulans and S. cerevisiae ACSs are in boldface and italicized. (B) Domain organization of the N. crassa ACSs. (C) Conserved amino acid sequences of putative N. crassa ACSs. Boldface and underlined amino acids within motifs I and II show the phosphate binding and linker domains, respectively. LC, long chain; VLC, very long chain.