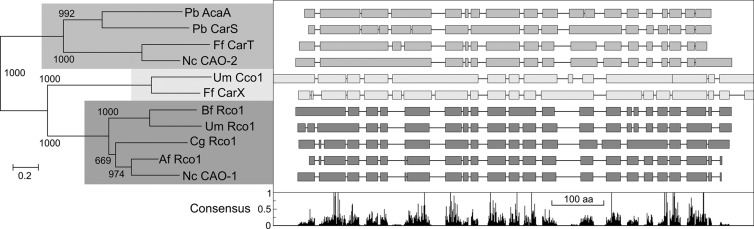
Fig 2.
Sequence analysis of CAO-1 (NCU07008) and other already characterized fungal CCOs. (Left) Neighbor-joining phylogram of 11 proteins, as follows: AcaA and CarS from Phycomyces blakesleeanus (genes 77754 and 79747, respectively, in its genome database), CarT (accession number CAL90971) and CarX (CAH70723) from Fusarium fujikuroi, CAO-2 from Neurospora (NCU11424), Cco1 (UM00965) and Rco1 (UM05084) from Ustilago maydis, and Rco1 from Botryotinia fuckeliana (XP_001548426), Chaetomium globosum (XP_001219451), and Aspergillus fumigatus (XP_746307). The shaded areas distinguish three major groups according to the enzymatic reaction. Top, four enzymes that cleave asymmetrically diverse carotenoid substrates; middle, two enzymes that cleave β-carotene symmetrically; bottom, resveratrol-cleaving enzymes with no known activity on carotenoid substrates. (Right) Simplified representation of the Clustal comparison between the proteins indicated on the left. Interruptions indicate gaps introduced by the Clustal program to facilitate alignment. The diagram below plots the proportion for the presence of the consensus amino acid (aa) at each position.