Fig 2.
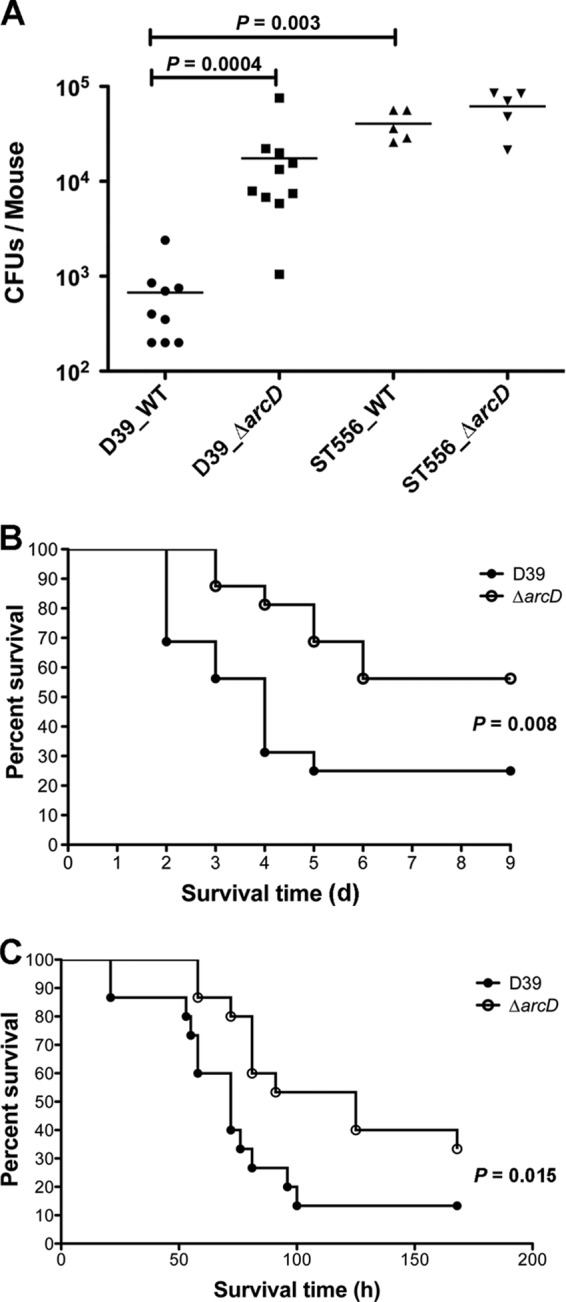
Role of ArcD in the virulence of S. pneumoniae D39. (A) Nasopharyngeal colonization of BALB/c mice infected with the WT and the ΔarcD mutant of D39 (n = 10) and ST556 (n = 5). Bacteria (∼2 × 106 CFU) in 20 μl of PBS were inoculated intranasally. Colonized bacteria were collected from the nasopharyngeal lavage fluid 5 days postinfection and were enumerated by plating serial dilutions. One mouse in the D39 WT group succumbed shortly after inoculation. Bars indicate the mean values. (B) Survival of mice during pneumococcal lung infection. BALB/c mice (n = 16) were challenged with the D39 WT and its ΔarcD mutant intranasally using ∼5 × 106 CFU of bacteria. The mice were monitored for up to 9 days (d) postinoculation. (C) Survival of mice during pneumococcal bacteremia. CBA/N mice (n = 15) were administered the D39 WT and its ΔarcD mutant intravenously using ∼2 × 105 CFU of bacteria. The mice were monitored for up to 7 days postinfection.
