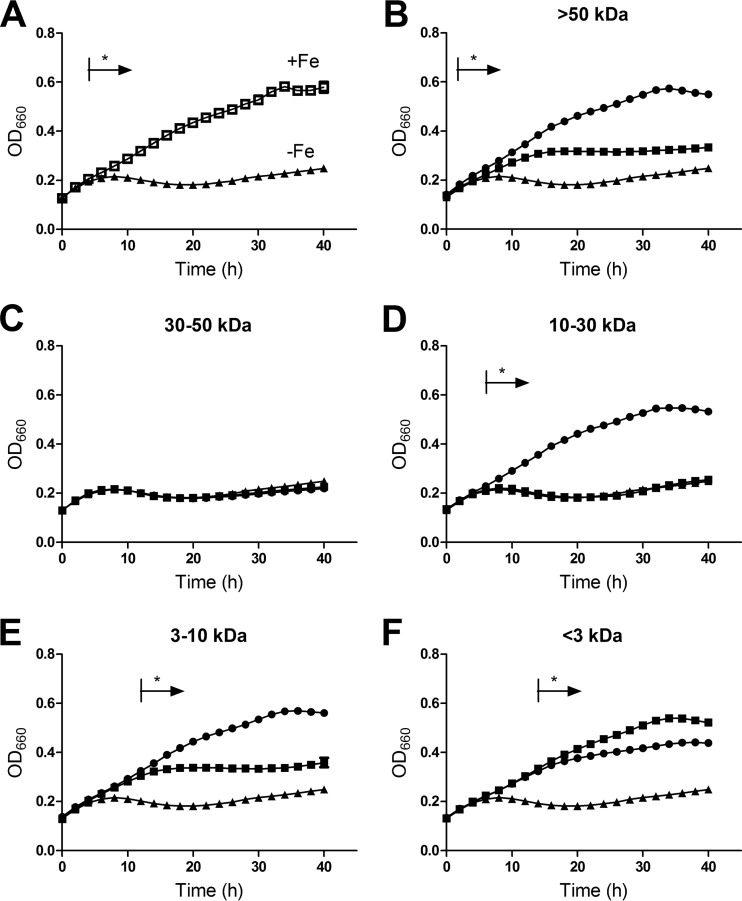
Fig 6.
Effect of HGA-melanin on L. pneumophila growth under iron-limited conditions. Wild-type strain 130b that had been grown in non-iron-supplemented BYE was inoculated into deferrated CDM that was supplemented with an additional aliquot of deferrated CDM (black triangles), standard CDM which contains iron (open squares, in panel A only), or a CDMP culture supernatant fraction that was obtained from 130b (black circles) or the lly mutant NU408 (black squares) and that was either >50 kDa (B), 30 to 50 kDa (C), 10 to 30 kDa (D), 3 to 10 kDa (E), or <3 kDa (F) in size. Samples were incubated at 37°C for up to 40 h, and bacterial growth was monitored by measuring the OD660 of the cultures. Data are the means and standard deviations from 3 to 4 replicates, although all the error bars are too small to be seen above the data point symbols. In panels B, D, and E, the cultures treated with the melanin-containing supernatant fractions from the wild type grew better than did those cultures supplemented with either supernatant material from the lly mutant or deferrated CDM (*, P < 0.05). In panel F, the cultures treated with the fraction from the mutant grew better than did those cultures supplemented with either supernatant material from the wild type or deferrated CDM (*, P < 0.05).