Fig 9.
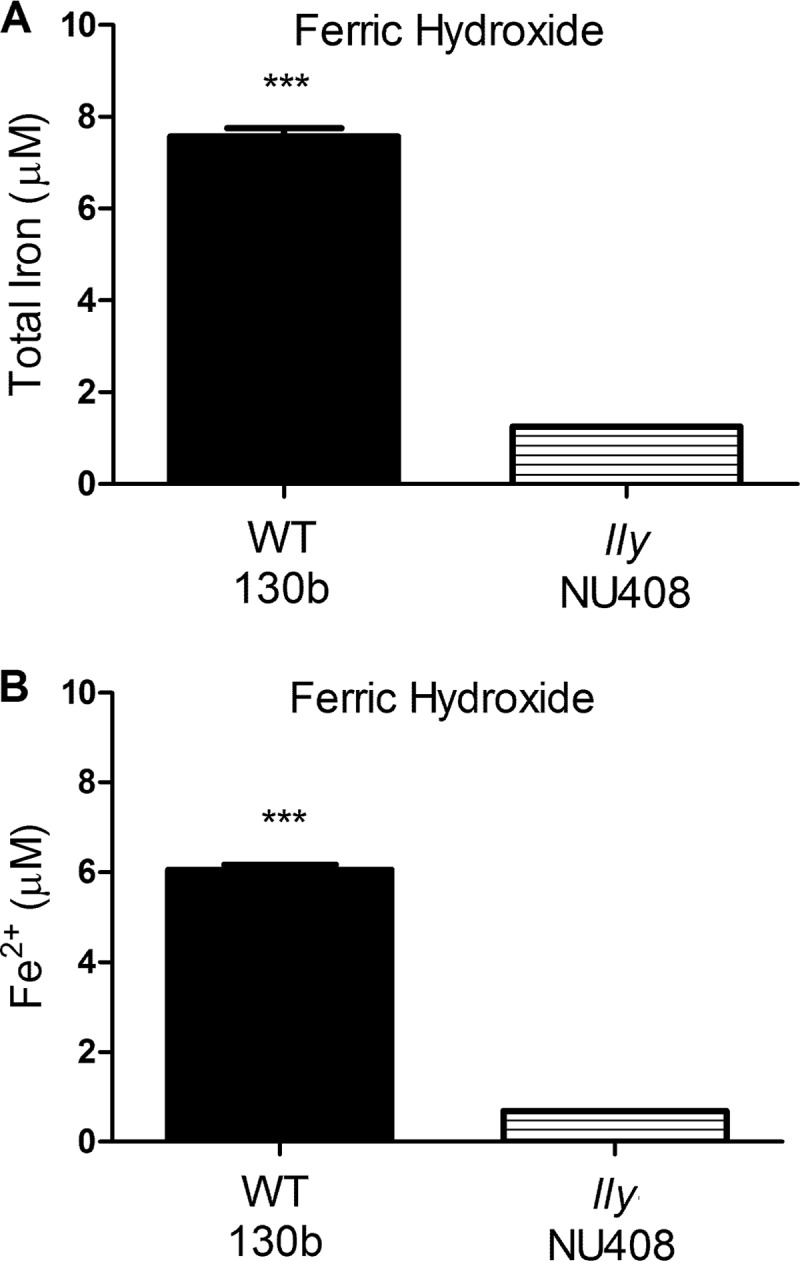
Effect of bacterial HGA-melanin on ferric hydroxide. As indicated, wild-type strain 130b and lly mutant strain NU408 were grown in CDMP containing added ferric hydroxide (1%, wt/vol), and then after 72 h of incubation at 37°C, the levels of total iron in cell-free culture supernatants were determined by the ferrozine assay in the presence of the reducing agent vitamin C (A) and the level of ferrous iron in cell-free supernatants was ascertained by the ferrozine assay in the absence of vitamin C (B). Data are the means and standard deviations obtained from triplicate samples. The levels of iron released into the supernatant were greater for the wild type than the mutant (***, P < 0.001).
